Cytoplasmic Determinants And Asymmetric Cell Division
Notably stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells. One copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate.
Asymmetric Cell Division An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Intrinsically cytoplasmic cell fate determinants eg Numb are asymmetrically localized within a cell and segregate differentially into daughters that adopt different fates reviewed by Yamashita 2009.
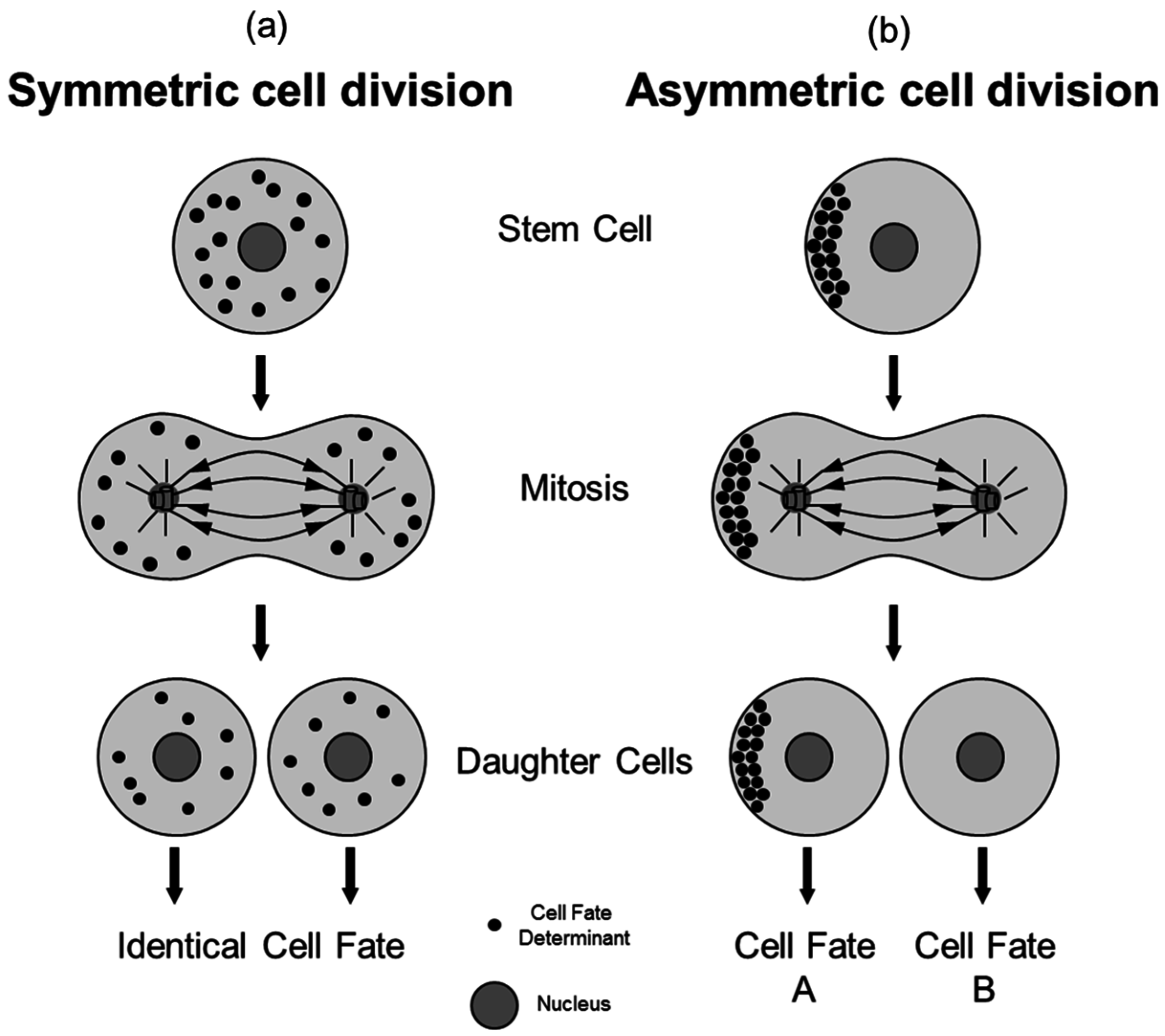
Cytoplasmic determinants and asymmetric cell division. Asymmetric cell divisions occur repeatedly during plant development but the mechanisms by which daughter cells are directed to adopt different fates are not well understood 12. Below we explain how different daughter cell. Previous studies have demonstrated roles for positional information in specification of daughter cell fates following asymmetric divisions in the embryo 3 and root 4.
Receptor-independent activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by the Drosophila GoLoco protein Partner of Inscuteable seems to represent a novel mechanism to control these events. Alternatively they can orient their division plane so that only one of the two daughter cells. Asymmetric cell division gives rise to daughter cells with distinct development fates.
Cytoplasmic determinants and asymmetric cell division - 6603061 1. Sristi9083 11112018 Biology Secondary School 13 pts. Asymmetric cell division depends on the polarization of the dividing cell for the correct alignment of the mitotic spindle and the localization of cytoplasmic determinants.
We begin with the first asymmetric division in the C. To achieve this remarkable task they can undergo an intrinsically asymmetric cell division whereby they segregate cell fate determinants into only one of the two daughter cells. How Do Cytoplasmic Determinants Affect Cell Differentiation.
Cells divide asymmetrically in response to extrinsic or intrinsic fate determinants. The scarecrow mutation results in roots that are missing one cell layer owing to the disruption of an asymmetric division that normally generates cortex and endodermis. A cell division is considered asymmetric when the two daughter cells have different sizes when one or more cellular constituents are preferentially segregated into only one of the two daughter cells or when the two daughter cells are endowed with different potentials to differentiate into a particular cell type Horvitz and Herskowitz 1992.
It is therefore of fundamental importance. What are Cytoplasmic Determinants Definition Types Function 2. In the Arabidopsis root meristem initial cells undergo asymmetric divisions to generate the cell lineages of the root.
Unequally inherited cytoplasmic determinants. In dividing cells this leads to asymmetric cell division in which each of the daughter cells differentiates into a different cell type. Elegans embryo where symmetry is broken by the local inactivation of actomyosin cortical contractility.
See bicoid cytoplasmic localization maternal effect gene maternal polarity mutants pole plasm. Stem cells self-renew but also give rise to daughter cells that are committed to lineage-specific differentiation. This contributes to establishing a polarized distribution of PAR proteins and associated components on the cell cortex along the longitudinal embryonic axis which becomes the anterior-posterior AP axis.
Thereafter AP polarity is maintained through reciprocal negative interactions between the anterior and posterior cortical domains. Tissue-specific markers indicate that a heterogeneous cell type is formed in the mutant. In animal cells the mitotic spindle determines the plane of cell division thus affecting cell size the position of daughter cells and the segregation of cytoplasmic determinants during the asymmetric division of polarized cells Doe and Bowerman 2001.
To divide asymmetrically a cell must position the mitotic spindle relative to localized cell fate determinants. Along with the cytoplasmic determinants signaling cascades are also involved in the cell differentiation during the embryonic development stage. Answered Cytoplasmic determinants and asymmetric cell division 2 See answers Answers.
An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates. Cytoplasmic determinants are also found in some post-embryonic cells where they produce cytoplasmic asymmetry qv. Recent work in the early ascidian embryo reveals the function of a single factor that coordinates this act to control cleavage pattern and cell fate determination.
Also called localized cytoplasmic determinants or morphogenetic determinants. Extrinsically daughter cells placed in different microenvironments adopt different fates. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise to daughter cells of equivalent fates.
Cytoplasmic Determinants Steemit
A Brand Asymmetric Cell Division
Dividing Cellular Asymmetry Asymmetric Cell Division And Its Implications For Stem Cells And Cancer
Model Systems In Which To Analyze Asymmetric Cell Division A Download Scientific Diagram
Asymmetric Cell Division Microtubule Dynamics And Spindle Asymmetry Journal Of Cell Science
Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
How Do Cells Become Specialized Pediaa Com
Introduction To Development Article Khan Academy
Dare To Be Different Asymmetric Cell Division In Drosophila C Elegans And Vertebrates Current Biology
Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html
What Is The Difference Between Cell Determination And Cell Differentiation Pediaa Com
Fate Of Cells The Developing Embryo Undergoes Morphogenesis In Order To Create Different Tissues And Organs Through Cleavage Gastrulation And Organogenesis Ppt Video Online Download
Morphogens Induction And Cytoplasmic Determinants
Factors That Influence Development Animal Reproduction And Development And Behavior
How Do Cytoplasmic Determinants Affect Cell Differentiation Pediaa Com
Cytoplasmic Determinant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Differentiation And Asymmetric Divison Ppt Download
