Asymmetric Cell Division Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a cell changes from one cell type to another. Alternatively they can orient their division plane so that only one of the two daughter cells.
Phase Separation In Asymmetric Cell Division Biochemistry X Mol
In times of growth or regeneration stem cells can also divide symmetrically to produce two identical copies of the original cell.
Asymmetric cell division cellular differentiation. Asymmetric stem cell division is a mechanism that balances stem cell self-renewal and differentiation through the production of one stem cell and one differentiating cell. Below we explain how different daughter cell. Notably stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells.
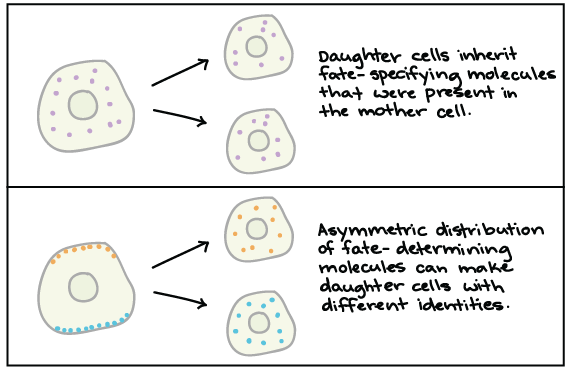
Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. A cell division is considered asymmetric when the two daughter cells have different sizes when one or more cellular constituents are preferentially segregated into only one of the two daughter cells or when the two daughter cells are endowed with different potentials to differentiate into a particular cell type Horvitz and Herskowitz 1992. Cellular differentiation is the process in which a cell changes from one cell type to another.
Stem cells self-renew but also give rise to daughter cells that are committed to lineage-specific differentiation. Symmetric and asymmetric stem cell divisions. Part of the Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation book series RESULTS volume 61 Log in to check access.
Usually the cell changes to a more specialized type. Our results suggest that both microtubules and a lipophilic site are important in the nuclear migration to one end of the spore prior to asymmetric cell division. Failure to properly control cell division mode may result in premature depletion of the stemprogenitor cell pool or abnormal growth and impaired differentiation.
Asymmetric cell division which generates daughter cells with distinct characteristics is a mechanism for creating complex systems through cellular differentiation. Cellular Mechanisms to Achieve a Symmetric Cell Division. To achieve this remarkable task they can undergo an intrinsically asymmetric cell division whereby they segregate cell fate determinants into only one of the two daughter cells.
Usually the cell changes to a more specialized type. Damian Dudka Patrick Meraldi. The balance between self-renewal and differentiation is achieved through control of cell division mode which can be either asymmetric or symmetric.
Asymmetric cell division ACD is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism used by prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike to control cell fate and generate cell diversity. One copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate. A Comparative Perspective on Wntv-Catenin Signalling in Cell Fate Determination.
Two studies in this issue. One strategy by which SCs can perform these two tasks is asymmetric cell division whereby upon SC division one daughter cell retains the cellular identity of its mother whereas its sister differentiates. In the asymmetric division model a stem cell produces one differentiated cell and one stem cell.
In the symmetric division model a stem cell produces two differentiated cells or two stem cells. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create. It is a simple way of maintaining the stem cell population without increasing it and is thus thought to be a vital mechanism for tissue homeostasis and tumor suppression.
Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create. A detailed mechanistic understanding of ACD is therefore necessary to understand cell fate decisions in health and disease.
The germination of Onoclea spores is a model system with many advantages for the study of asymmetric cell division and cellular differentiation.
Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
What Are Stem Cells Stammzellnetzwerk Nrw
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Divisions In The Asymmetric Download Scientific Diagram
Lessons From Development A Role For Asymmetric Stem Cell Division In Cancer Sciencedirect
Symmetric Asymmetric Division Of A Cancer Stem Cell Asymmetric Cell Download Scientific Diagram
Stem Cell Self Renewal Proliferation And Differentiation Stem Cells Download Scientific Diagram
Fig 2 1 Schematic Presentation Of Stem Cell Function A The Differentiation Potential Of A Stem Cell Determines Its Potency B The Balance Between Symmetric And Asymmetric Cell Divisions Regulates Stem Cell Self Renewal
Centrosome Segregation During Asymmetric Cell Division A Abscission Download Scientific Diagram
Asymmetric Cell Division In C Elegans Cherry Biotech
Asymmetric Cell Division In Land Plants And Algae The Driving Force For Differentiation Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
Cell Differentiation Tissue Learn Science At Scitable
Solved What Are The Main Differences Between Symmetric An Chegg Com
Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html
Principles And Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Cell Division Development
Asymmetric Cell Division An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Introduction To Development Article Khan Academy
Basl Controls Asymmetric Cell Division In Arabidopsis Cell
Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Cell Division In Epithelial Cells Schematic Download Scientific Diagram
Pdf Asymmetric Cell Division Recent Developments And Their Implications For Tumour Biology Semantic Scholar
