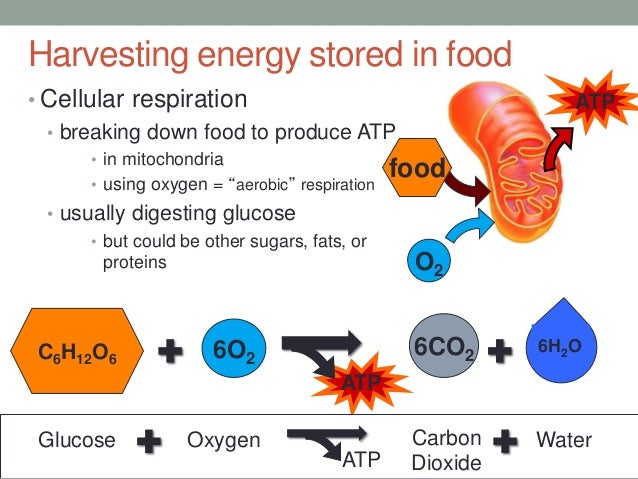
How Animal Cells Use Nutrients To Provide The Energy For Growth Movement And Cell Division
Carbohydrates are the basic source of energy for all animals. Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells.
Sources of energy and of all the materials for the renewal or synthesis of protoplasm must be available to the cells.
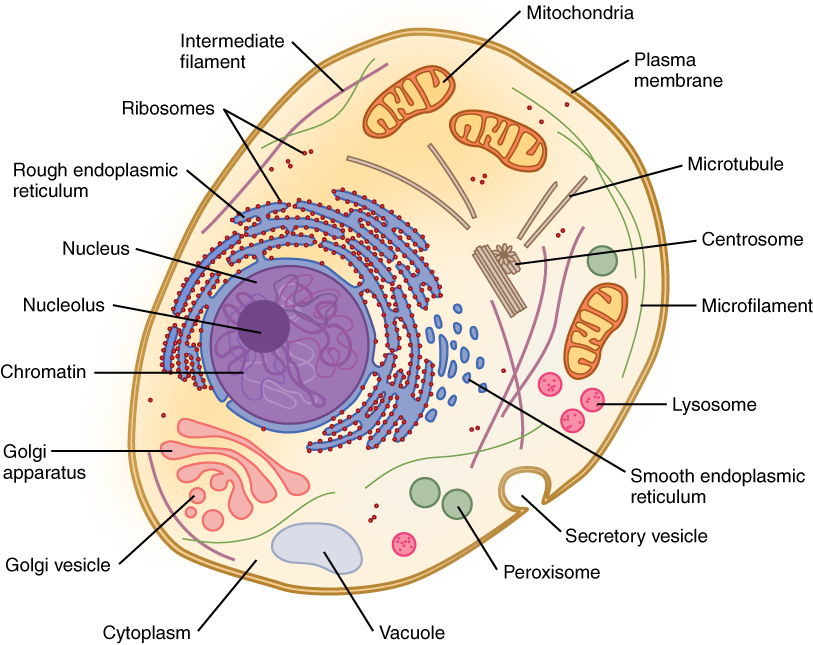
How animal cells use nutrients to provide the energy for growth movement and cell division. The membrane is partially permeable which allows certain molecules to diffuse across them. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell on the left viewed with the light. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell on the left viewed with the light.
Because embryonic cells have proved to be such convenient experimental material the knowledge of cell nutrition relates preponderantly to these cells of high. Carbohydrates or sugars are the primary source of organic carbons in the animal body. Animal cells use chemical energy from the breakdown of molecules they consume to drive the build up of molecules they want through cellular respiration.
Animal and plant cells also have cell membranes. How Animals Absorb Nutrients and Dispose of the Rest Nutrients that the body can use are absorbed into the cells lining the small intestine. Cells grow divide and take in nutrients which they use to provide energy for cell functions All life and therefore all cells are characterized by a number of basic functions.
The rest of the material that cannot be further digested or used passes onto the large intestine. Complex carbohydrates including polysaccharides can be broken down into glucose through biochemical modification. They also convert this chemical energy into the mechanical energy of movement.
This is another process in which animal and plant cells differ. During digestion digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy through metabolic pathways. Animals obtain their carbohydrates from the external environment compared with plants which synthesize carbohydrates by photosynthesis.
Passive and active transport utilize small proteins embedded in the cell membrane to allow a nutrients passage whereas endocytosis involves engulfing a nutrient. They generate energy for the cell in the form of ATP. In animal cells cytokinesis is achieved through the constriction of the cell by a ring of contractile microfilaments consisting of actin and myosin the proteins involved in muscle contraction and other forms of cell movement.
All of which creates a lot of heat. Finally both also have ribosomes for protein synthesis. However humans do not produce the enzyme cellulase and lack.
Nutrients enter the cell through the cell membrane. Oxygen is needed for this process known as respiration. The nutrients used by animals include carbohydrates lipids nucleic acids proteins minerals and vitamins.
Carbohydrates or sugars are the primary source of organic carbons in the animal body. Animal cells have a basic structure. Worthy nutrients remain in your system.
During digestion digestible carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into glucose and used to provide energy through metabolic pathways. Cells got energy by. Nutrients must first be broken down through chewing and enzymes located in both the stomach and small intestine.
The organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food. Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells. The organic molecules required for building cellular material and tissues must come from food.
Animal cells have a basic structure. Cells need to replicate or reproduce materials need to move into and out of a cell and the cell must obtain energy and use energy. The cell converts the nutrients into the energy.
Mitochondria is the main site for energy release during respiration. The membrane controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The needs of the cells for prolonged maintenance may prove fewer in number and simpler in structure than assumed.
This energy is used by the cell for cell division growth and repair. The excess sugars in the body are converted into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles for later use. Glycogen stores are used to fuel prolonged exertions such as long.
 The Nucleus And Cytoplasm Anatomy And Physiology
The Nucleus And Cytoplasm Anatomy And Physiology

 Nutrient Metabolism Human Learn Science At Scitable
Nutrient Metabolism Human Learn Science At Scitable
 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Cbse Notes For Class 11 Biology 10 Biology Notes Cell Cycle Cell Division
Cell Cycle And Cell Division Cbse Notes For Class 11 Biology 10 Biology Notes Cell Cycle Cell Division
 Nutrient Cycles Nutrient Cycle Organic Molecules Energy Pyramid
Nutrient Cycles Nutrient Cycle Organic Molecules Energy Pyramid
 Silicon Strengthens Plant Cell Walls Which Provides Protection Against Pests Diseases And Lodging Silicon Optimizes Nutrient The Cell Cell Wall Animal Cell
Silicon Strengthens Plant Cell Walls Which Provides Protection Against Pests Diseases And Lodging Silicon Optimizes Nutrient The Cell Cell Wall Animal Cell
Nutrition And Energy Production Boundless Biology
 Eukaryotic Cells Learn Science At Scitable
Eukaryotic Cells Learn Science At Scitable
 Characteristics Of Living Things Bundled Characteristics Of Living Things Microbiology Study Characteristics
Characteristics Of Living Things Bundled Characteristics Of Living Things Microbiology Study Characteristics
 Most Dinoflagellate Species Live In The Marine Environment Zooxanthellae Is An Example Of Dinoflagellates Th Life Cycles Symbiotic Relationships Cell Division
Most Dinoflagellate Species Live In The Marine Environment Zooxanthellae Is An Example Of Dinoflagellates Th Life Cycles Symbiotic Relationships Cell Division
 Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Mitochondria Eukaryotic Cell Mitochondria Cellular Respiration
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Mitochondria Eukaryotic Cell Mitochondria Cellular Respiration
 Metabolism Basic Concepts And Design Ppt Download
Metabolism Basic Concepts And Design Ppt Download
Energy Cycle From Plants To Animals
 Mastering A P Chapter 3 Cells The Living Units Diagram Quizlet
Mastering A P Chapter 3 Cells The Living Units Diagram Quizlet
 The 7 Cell Functions 1 Movement Muscle Cells 2 Conductivity Nerve Cells 3 Metabolic Absorption Kidney Cell Structure Animal Cell Human Cell Structure
The 7 Cell Functions 1 Movement Muscle Cells 2 Conductivity Nerve Cells 3 Metabolic Absorption Kidney Cell Structure Animal Cell Human Cell Structure
 Pin On Teaching Apologia Biology
Pin On Teaching Apologia Biology
 Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
 Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable
Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable