Cell Division Occurs In Embryology
The embryoblast divides into the epiblast and hypoblast forming a two-layered structure. Initially the zygote splits along a longitudinal plane.
Pin On Zoologia Od Gr Zῷon Zoon Zwierze I Logos Logos Slowo Nauka
The blastula contains a cavity named blastocoel and its outer covering is designated as blastoderm.
Cell division occurs in embryology. The cells which are produced during segmentation are called blastomeres. During cell division a cell divides into two daughter cells mitosis or four daughter cells meiosis. These early divisions produce separate cells called.
The genetic material of the. Cell division produces new cells from pre-existing ones in order to help in growth replacement repair and reproduction in all living organisms. The second division is also longitudinal but at 90 degrees to the plane of the first.
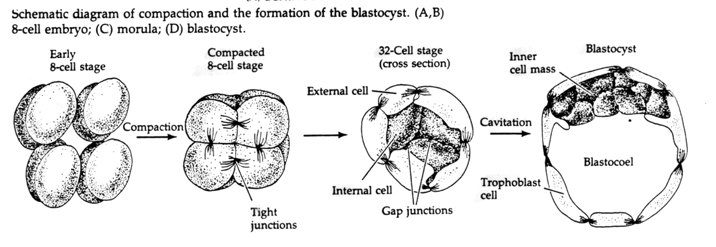
Because these cells arise only through the cleavage of the zygote and all are found inside the pellucid zone which cannot expand no growth is seen. Approximately 24 hours after fertilization the impregnated oocyte begins with the first cleavage division. The morula a collection of around 30 cells blastomere is created at about 96 hours.
Start studying Cell Division and Embryology. In developmental biology cleavage is the division of cells in the early embryo. During this process the parent cell is diploid 2n and gametes sperm and ovum are haploid n.
Cleavage ends with the format. Neural crest cells are sometimes called the fourth germ cell layer and derive from a group of specialized cells that reside adjacent to the crest of the neural ridge during neurulation. Historically the cells produced by this division are called daughter cells.
These are exactly similar to each other as well as resemble the parent cell. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage in embryology the first few cellular divisions of a zygote fertilized egg.
At first the cells remain closely associated but later on they form the lining of a hollow sphere called blastula. Note that DNA duplication replication occurs during interphase S phase before mitosis and not during mitosis. Cleavage consists of division of the zygote into a large number of cellular entities.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The third division is perpendicular to the first two and is equatorial in position. The process follows fertilization with the transfer being triggered by the activation of a cyclin-dependent kinase complex.
Neural crest cells then migrate extensively into the cranium trunk vagal and sacral regions and heart. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. Mitosis is the form of cell division in all cells except germ cells occurs by 2 mechanical processes that initially divide the nucleus then the cell cytoplasm.
Embryology deals with the study of embryogenesis which includes the developmental processes between fertilization and birth or hatching and can be divided into three distinct stages cleavage gastrulation and organogenesis. In biological terms the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Each mitosis of a diploid cell produces 2 diploid cells.
The formation of blastula culminates the cleavage period. During the second week the trophoblast and embryoblast divide into increasingly specialised cell types. This process produces two daughter cells that should be genetically identical to the parent cell.
Their migration is associated with down-regulation of N-cadherin expression. Normal cell division in all cells except germ cells occurs by 2 mechanical processes that initially divide the nucleus then the cell cytoplasm. This is the process in which the egg and sperm cell production occurs and it only occurs in gonads ovary and testes.
The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell. Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis refers to the development and formation of the human embryo.
Outer cell mass trophoblast contacts with the endometrium of the uterus to facilitate implantation and the formation of the placenta. This process results in cells only having half the number of chromosomes of parent cell. The trophoblast divides into the syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast.
Inner cell mass embryoblast responsible for the formation of the embryo itself.
Germ Layer Definition Primary Layers Embryonic Development Britannica
Ch28 Embryonic Development Birth Estudio
Neural Crest Development Embryology
Embryonic Disc Google Search Cavities Membrane Disc
Second Third Week Of Embryonic Development Chorion Types Of Chorionic Villi Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology Physiology
Cardiovascular System Blood Development Embryology
Irocket Learning Module Embryology Basics Embryonic Development Development Nursing Students
Primordial Germ Cell Development Embryology
Pin On Https Drawittoknowit Com
Development Of Human Embryonic Tissues Medical School Studying Diagnostic Medical Sonography Nursing Study Guide
Embryology Embryogenesis Human Development And Stages Of Pregnancy
214260 Jpg Visuals Unlimited Macro And Micro Science And Nature Mitosis
Pin By Draw It To Know It Medical On Https Drawittoknowit Com Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Mcat Study
Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Human Embryogenesis Article Embryology Khan Academy
Blastocyst Development Embryology
Cytokinesis Bioninja Cell Wall Plant And Animal Cells Plant Cell
