Rate Of Cell Division In Cancer
These are called secondary tumours. So we can assume that 124h is the maximum rate of cell division by cancer.
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Cancer is somewhat like an evolutionary process.
Rate of cell division in cancer. These processes - cell division and. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Sometimes cancer cells break off from the original tumour and spread in the blood to other parts of the body.
Cancer cells will form lumps or tumours that damage the surrounding tissues. Endgroup Karin VanMeter Oct 5 17 at 2222. Division rates can be inferred from cancer genome mutation frequencies and Equation.
They continue to replicate and make more tumours. Over time cancer cells accumulate multiple mutations in genes that control cell division. Originally tumours were thought to grow because they consisted of cells that multiplied more rapidly than cells in the surrounding tissue.
Although cancer incidence decelerates at advanced age in humans no deceleration occurs in mice. This lack of reduced proliferation rates in older mice may partially explain why mice do not have a deceleration in cancer incidence with increasing age as is seen in humans. They may form a lump or tumour which can cause damage to surrounding tissues and organs.
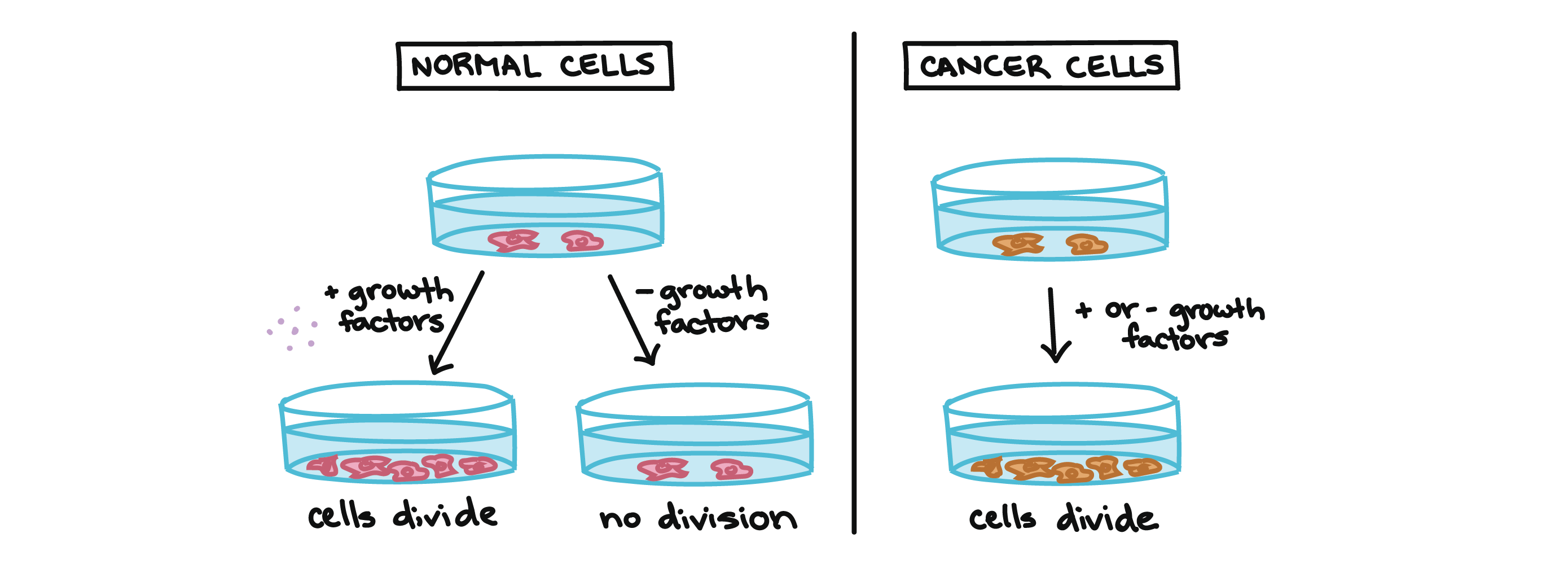
A Because cancer cells divide at a much higher rate than normal cells reducing the rate of cell division will slow the growth of the tumor. Cancer cells are able to replicate by overcoming the normal controls of cell division. The results of this are daughter cells that contain abnormal DNA or even abnormal numbers of chromosomes.
With a rate of 10 -9 mutations per base per division mutations accumulate with aging in mitotic tissues. Cell Division Rates Do Not Decelerate in Laboratory Mice. In addition most cells in an adult will be differentiated to serve a particular purpose.
For cell division to occur the two sets of DNA must be. 11 begingroup My first thought was this. Begingroup This is very difficult to answer since the rate of cell division is age and also health dependent.
Learn how dangerous this accumulation can be. If one cell has an incomplete copy of the DNA or if the DNA becomes damaged genetic disorders and diseases such as cancer can result. Cancer cells can divide without receiving the all clear signalWhile normal cells will stop division in the presence of genetic DNA damage cancer cells will continue to divide.
How cancer can be linked to overactive positive cell cycle regulators oncogenes or inactive negative regulators tumor suppressors. When a tumour spreads to another part of the body it is said to have metastasized. Lets read more about cancer in vivo because it behaves completely different than immortalized cell lines in in vitro tests.
Cancer cells may spread from the original primary tumour to form new secondary tumours throughout the body. When this happens the tumour is said to have metastasized. Cells in tissue from the colon small intestine and esophagus of the older mice divided at 97 96 and 87 the rate of the younger mice respectively.
See full answer below. In this manner cancer cells can evolve. Cancer genomes generally have less than one somatic mutation per 100000 bases dotted line.
In a fully grown adult of course the rate of cell proliferation is much less and under normal circumstances cell division in an adult takes place only when signals indicate the need to grow or to replace cells that have been lost damaged or worn out. According to Wikipedia citation provided Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. We wondered whether this difference might reflect differences in stem cell division rates in older individuals of the 2 species 21 22.
These mutant cells are even more abnormal than the parent cell. Add a comment 1 Answer Active Oldest Votes.
Somatic Cell Division Somatic Cell Mitosis Cell Division
Cell Division Biology Library Science Khan Academy
Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
How Long Do The Different Stages Of The Cell Cycle Take
How Cancer Starts Grows And Spreads Canadian Cancer Society
7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
The Cell Cycle And Cancer Biology Class
Diagrams Cell Cycle Cell Division By Mitosis Meiosis Sexual Reproduction Haploid Diploid Chromosome Numbers Zygote Gametes Sperm Eggs Binary Fission Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Percentile Growth Charts Graphs Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology Revision Notes
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
Mitosis And Cytokinesis Hd Animation Playlist Interactive Science Notebook Mitosis Middle School Science Experiments
Pin By Pearlyjoubert On Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Tumor Suppressor
Cyclin Dependent Kinases Regulate Lysosomal Degradation Of Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1a To Promote Cell Cycle Progression Cell Cycle Gene Expression Hypoxia
Cell Cycle Regulators Article Khan Academy
Cell Division Cancer Learn Science At Scitable
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
Biointeractive Homepage Cell Cycle Biology Classroom Eukaryotic Cell
Leaf Anatomy Mitosis Cell Cycle Cell Division
