Conclusion Of Cell Cycle And Cell Division
These events include the duplication of its DNA DNA replication and some of its organelles and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. The period in which one cycle of cell division is completed is called cell cycle.
 Cell Cycle Game Ngss Next Generation Science Standards Mitosis Board Game High School Biology Mid Life Science Middle School Cell Cycle Biology Lessons
Cell Cycle Game Ngss Next Generation Science Standards Mitosis Board Game High School Biology Mid Life Science Middle School Cell Cycle Biology Lessons
Unicellular organisms like yeast reproduce by cell division whereas multicellular organisms like us use the same process to develop grow and maintain our tissues.

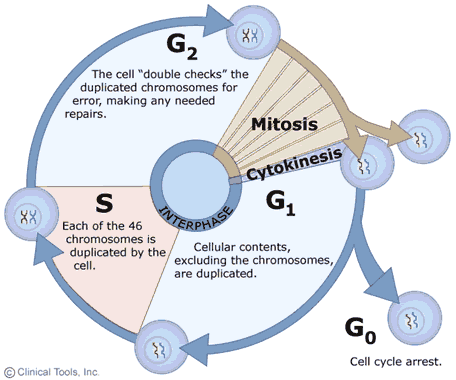
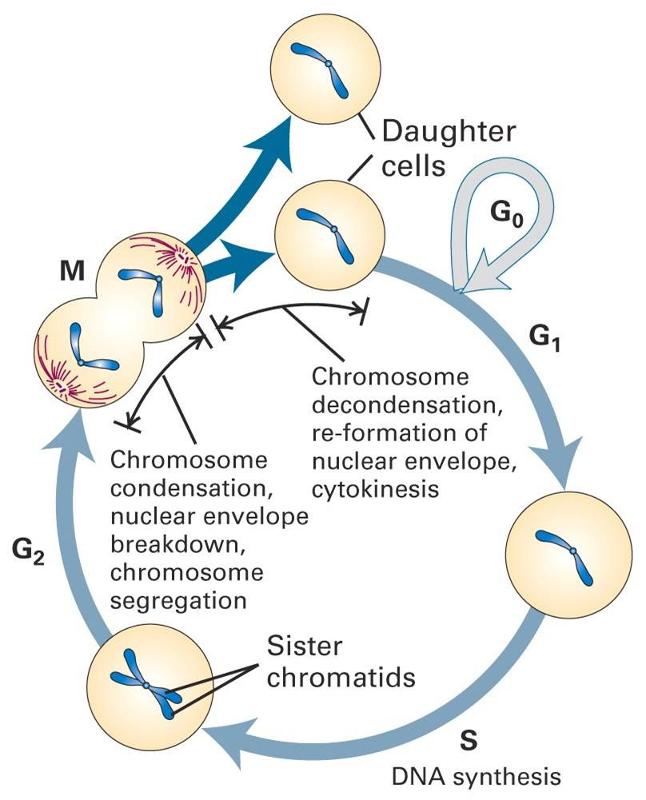
Conclusion of cell cycle and cell division. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasmThere are two kinds of nuclear division-mitosis and meiosis. In conclusion it is important to keep in mind that there are three types of cell division each of which plays a special purpose and achieves a given goal. 1Interphase DNA synthesis 2Mitotic phase Nuclear division INTERPHASE.
To observe the phases in mitosis and examine how they act together to create new daughter cells and determine the amount of time in each phase. During the division of each cell DNA of the cell replicate and after this growth of the cell takes place. It has two phases.
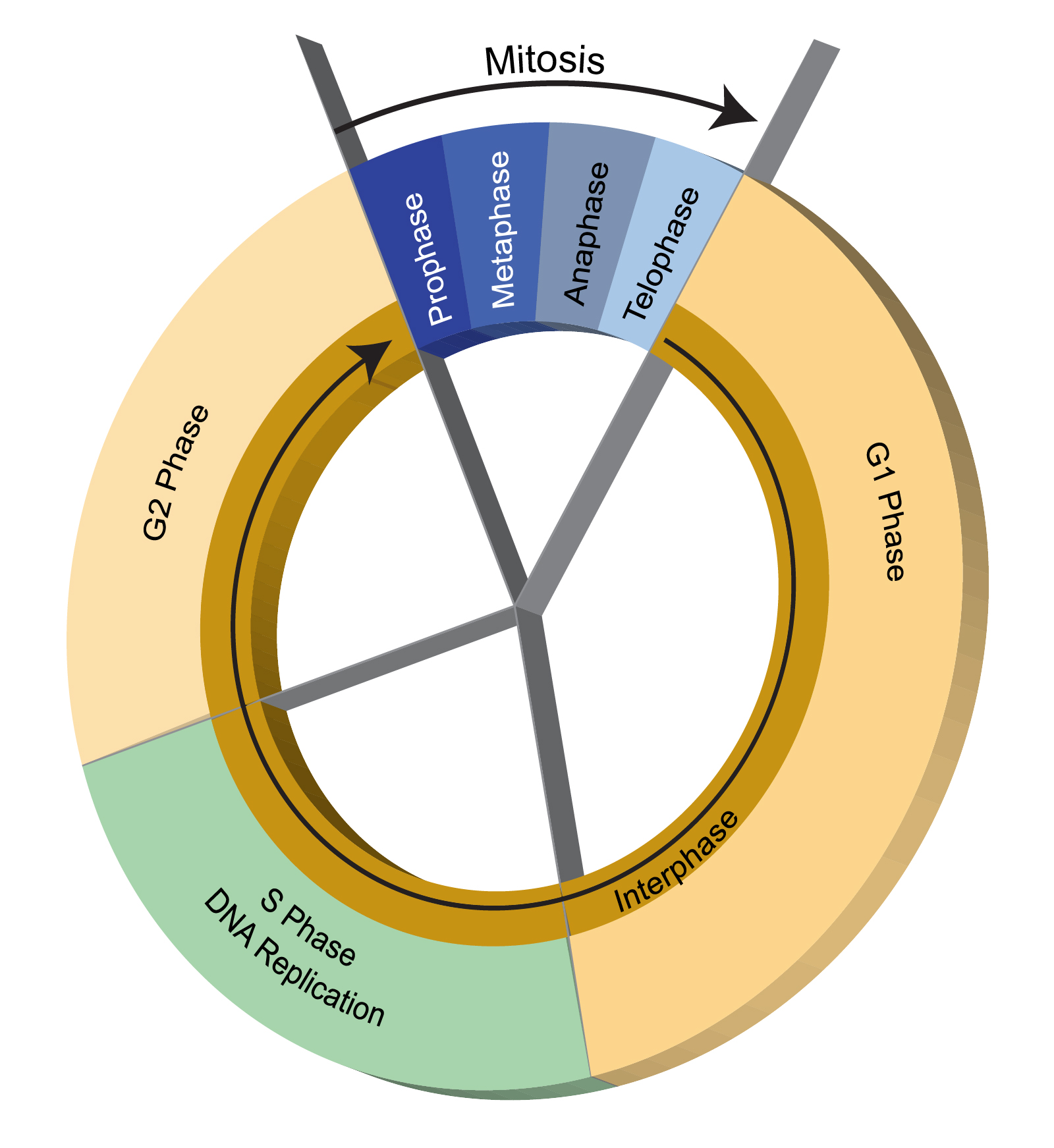
The cell cycle is composed of three periods. The interphase of the cell cycle is composed of G 1 S and G 2 phases. Prokaryotic cells have a single circular chromosome no nucleus.
It consists of two phases nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. How this happens depends on whether the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Cell division is a process by which one cell produces two or more daughter cells.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Cell division is simpler in prokaryotes than eukaryotes because prokaryotic cells themselves are simpler. Knowledge of what controls normal cell division is critical to understanding how disruption of this phenomenon can initiate pathological processes.
This duplication occurs for many reasons but mainly it is to replace old cells. This duplication occurs in many stages and has checkpoints along the way to make sure the cell is replicating as planned. In the cell all these processes must be performed in a well-harmonized way by ensuring correct division and formation of the progeny of the cells containing unchanged genomes.
This is a very important process and has varying implications from growth and development to repair of the organism. Prophase metaphase anaphase and the telophase. The cells in our body are highly intelligent.
Cell cycle period can vary from organism to. - In plants the cells that are. Cell division involves the distribution of identical genetic material DNA to two daughter cells.
The cell cycle comprises three co - ordinated processes of cell division DNA replication and cell growth. Mitotic division is composed of four phases. Cell division is a very noteworthy process in all living organisms.
They are interphase mitotic phase and the cytokinesis. The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. Essentially the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events that occur before the cell actually divides and gives rise to new cells.
It consists of - G1RNA protein synthesis SDNA synthesis G2RNA protein synthesis phases. Both cell cycle and cell division contain different but sequential periods of the cells life. They know when to duplicate themselves and when to rest or stop dividing altogether.
Mitotic division and cytokinesis are collectively called as the cell division. Telophase is followed by the. Mitosis is also important for the repair of damaged tissues and allows for growth.
Mitosis being the most common form of cell division is important for growth and repair since cells wear out and have to be replaced. Cell Cycle The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome synthesizes the cells other constituents and subsequently divides into two daughter cells is called the cycle of cells. Cell division is the process in which one cell called the parent cell divides to form two new cells referred to as daughter cells.
The Cell Cycle Duration Of The Cell Cycle Sparknotes
 Mitosis Learn Science At Scitable
Mitosis Learn Science At Scitable
 Vlab Cell Division By Sas Curriculum Pathways Cell Division Science Inquiry Mitosis
Vlab Cell Division By Sas Curriculum Pathways Cell Division Science Inquiry Mitosis
 The Cell Cycle Biology For Non Majors I
The Cell Cycle Biology For Non Majors I
 7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
 What Is The Purpose Of The Cell Cycle Socratic Cell Cycle Cell Division The Cell
What Is The Purpose Of The Cell Cycle Socratic Cell Cycle Cell Division The Cell
 Mitosis And Meiosis Science Escape Room Mitosis Meiosis Escape Room
Mitosis And Meiosis Science Escape Room Mitosis Meiosis Escape Room
 Model Of Meiosis Using Jelly Beans One Part Of A Longer Packet Which Included Additional Assessments Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
Model Of Meiosis Using Jelly Beans One Part Of A Longer Packet Which Included Additional Assessments Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle The Cell
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle The Cell
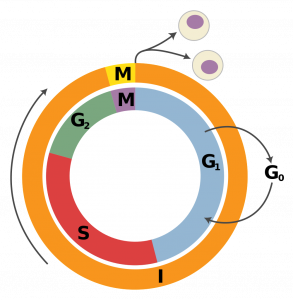 G1 And G2 What Happens In The Growth Phases Of The Cell Cycle
G1 And G2 What Happens In The Growth Phases Of The Cell Cycle
 Meiosis Mitosis Ensenanza Biologia Psicobiologia Estudiar Biologia
Meiosis Mitosis Ensenanza Biologia Psicobiologia Estudiar Biologia
 Mitosis And The Cell Cycle 7 Engaging Lab Station Activities Cell Cycle Mitosis Cell Cycle Activity
Mitosis And The Cell Cycle 7 Engaging Lab Station Activities Cell Cycle Mitosis Cell Cycle Activity
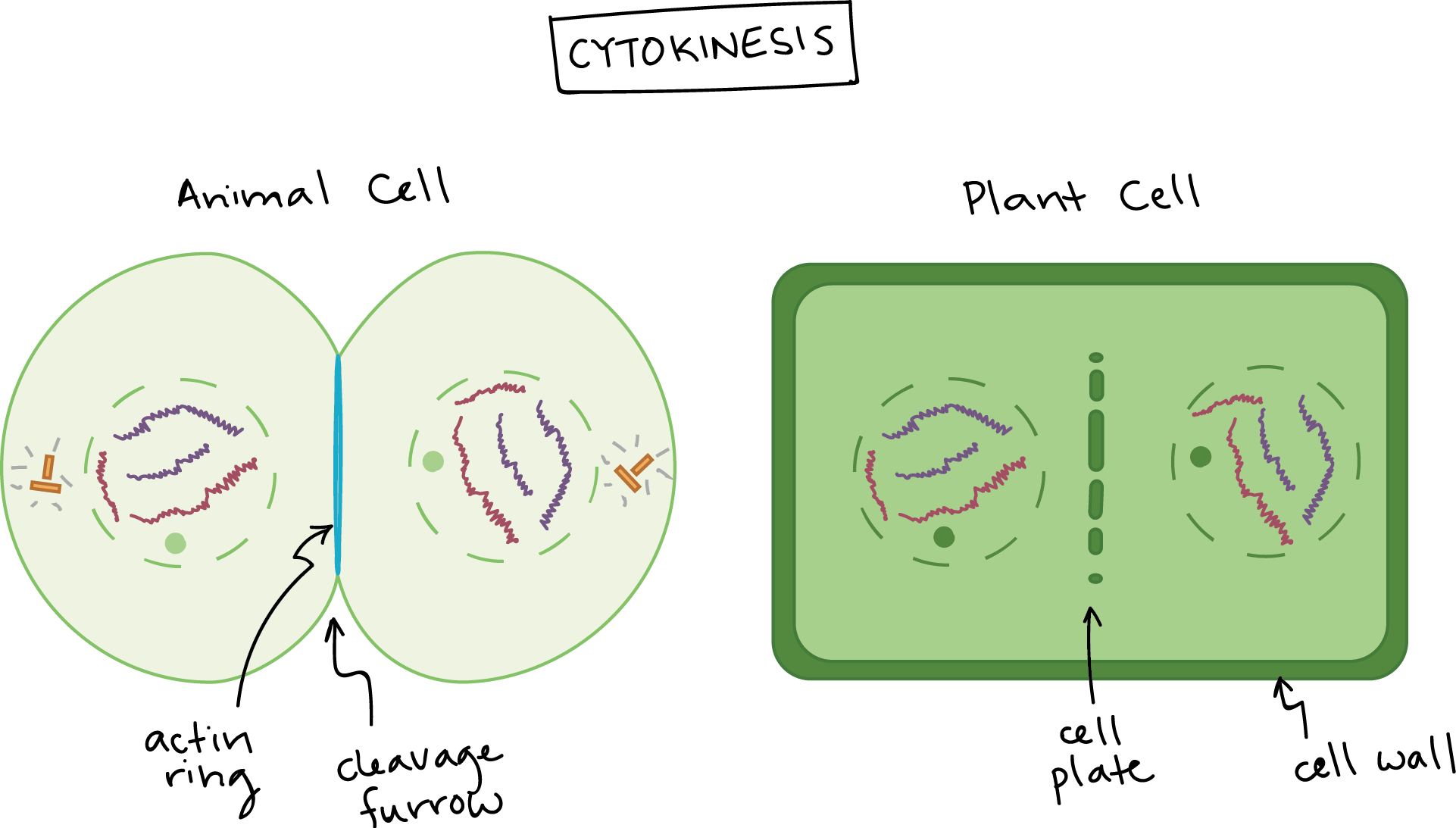 The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Review Article Khan Academy
The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Review Article Khan Academy
 Cell Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cell Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement