How Does Cell Division Help Organisms Grow
Multicellular organisms use cell division for growth and repair of damage such as wounds. Hence mitotic divisions of cells are required.
 Module 2 Part C Cell Division And Reproduction Cell Cycle Cell Division Organelles
Module 2 Part C Cell Division And Reproduction Cell Cycle Cell Division Organelles
Mitotic cell division enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from the one-celled zygote which itself was produced by meiotic cell division from gametes.

How does cell division help organisms grow. Bacteria grow to a fixed size. The dividing cell spends most of its time in interphase as it grows in preparation for cell division. In human bodies nearly two trillion cells divide every day.
Cell division solves the problem of increasing size by reducing the volume of cytoplasm in the two daughter cells and dividing up the duplicated DNA and organelles thereby increasing surface to volume ratio of the cells. A multicellular organism can only grow by adding more cells. Bacteria only have one chromosome.
This is achieved by the highly regulated process of cell proliferation. Coli bacteria cell bottom. The growth and division of different cell populations are regulated in different ways but the.
Unlike multicellular organisms increases in the size of bacteria cell growth and their reproduction by cell division are tightly linked in unicellular organisms. The cells must make copies of their chromosomes the information storing part of the cell before they split. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation.
Growth in these cells occurs only as a result of normal or pathological increases in. The mitosis phase of the cell division process involves the separation of nuclear chromosomes followed by cytokinesis division of the cytoplasm forming two distinct cells. After growth cell division by mitosis allows for continual construction and repair of the organism.
The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth then replication of DNA. Therefore they can split very simply by making a copy of the chromosome and making sure one chromosome ends up in each cell after it divides. Development again means adding more and more specialized cells to form tissues and.
In multicellular organisms it is the means of tissue growth and maintenance. The human body experiences about 10 quadrillion cell divisions in a lifetime. At this point many cells such as nerve or heart muscle cells no longer possess the ability to divide.
Watch cells divide in this time lapse video of an animal cell top and an E. Organisms grow either by augmenting cell size or increasing in cell number. Organisms grow because cells are dividing to produce more and more cells.
When cells are dividing they grow in size for a bit and then split in two. Cell division and growth. In human bodies nearly two trillion cells divide every day.
Multicellular organisms grow through cell division. Single celled organisms increase their numbers by dividing and making more cells like themselves. A growing and dividing cell goes through a series of stages called the cell cycle.
At the end of the mitotic cell cycle two distinct daughter cells are produced. Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell including both cytoplasmic nuclear and organelle volume. The new cells produced by cell division are genetically identical to the parent cell because they each.
In unicellular organisms cell division is the means of reproduction. Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation where a cell known as the mother cell grows and divides. While a multicellular organism is in its early stages of development cells divide at accelerated rates to increase the size of the organism.
Cells continue to divide to increase organism size until the organism reaches adulthood. The image above shows the process of animal cell division. Each cell contains identical genetic material.
Survival of the eukaryotes depends upon interactions between many cell types and it is essential that a balanced distribution of types be maintained. The single strand of DNA that. A multicellular organisms growth and development start with one cell which then divides into two cells.
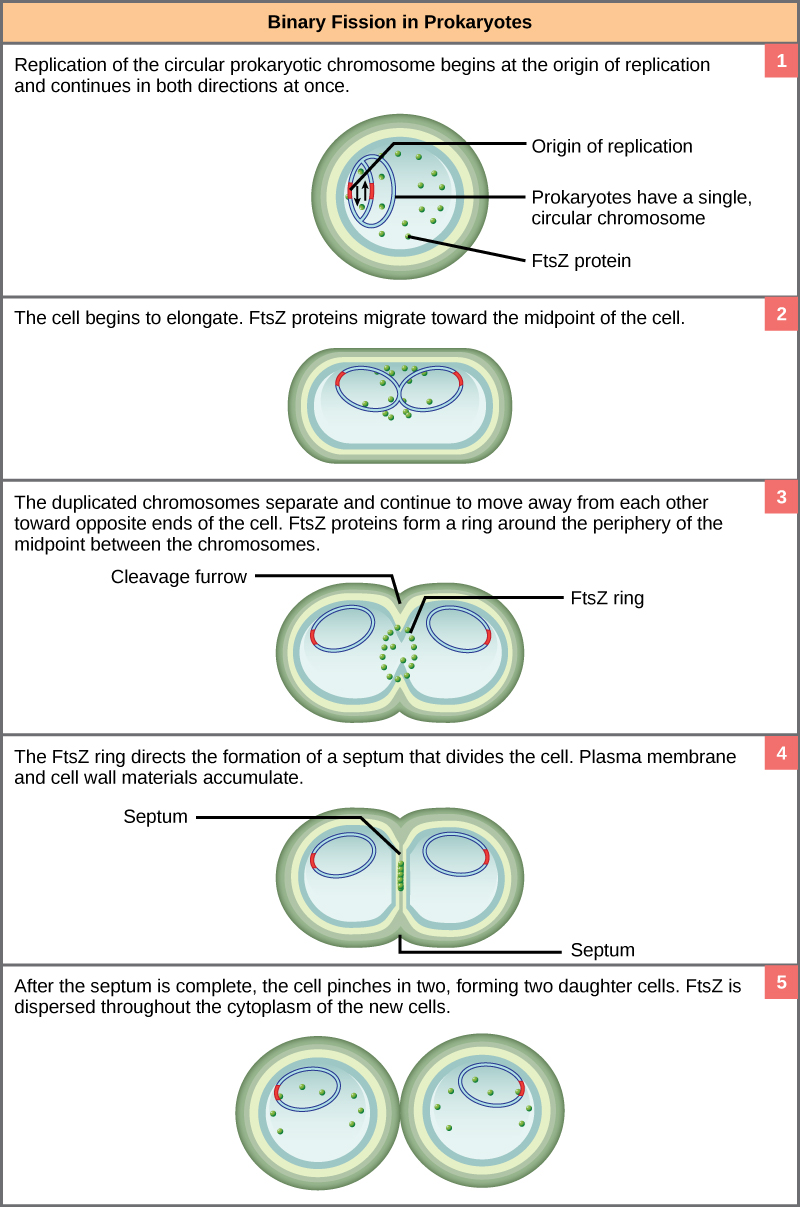 Prokaryotic Cell Division Biology I
Prokaryotic Cell Division Biology I
 Purpose Of Cell Division Biology Dictionary
Purpose Of Cell Division Biology Dictionary

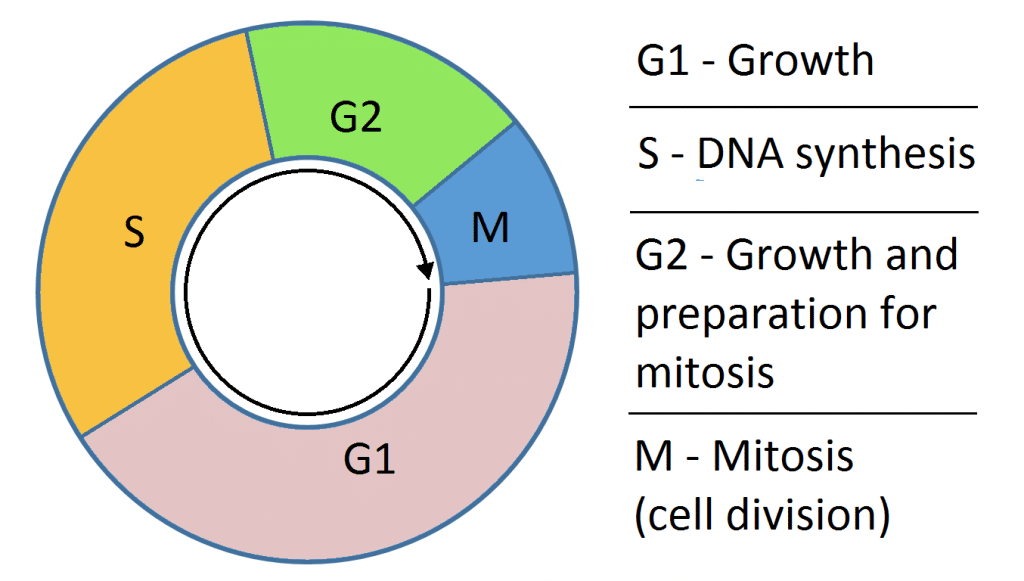 The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
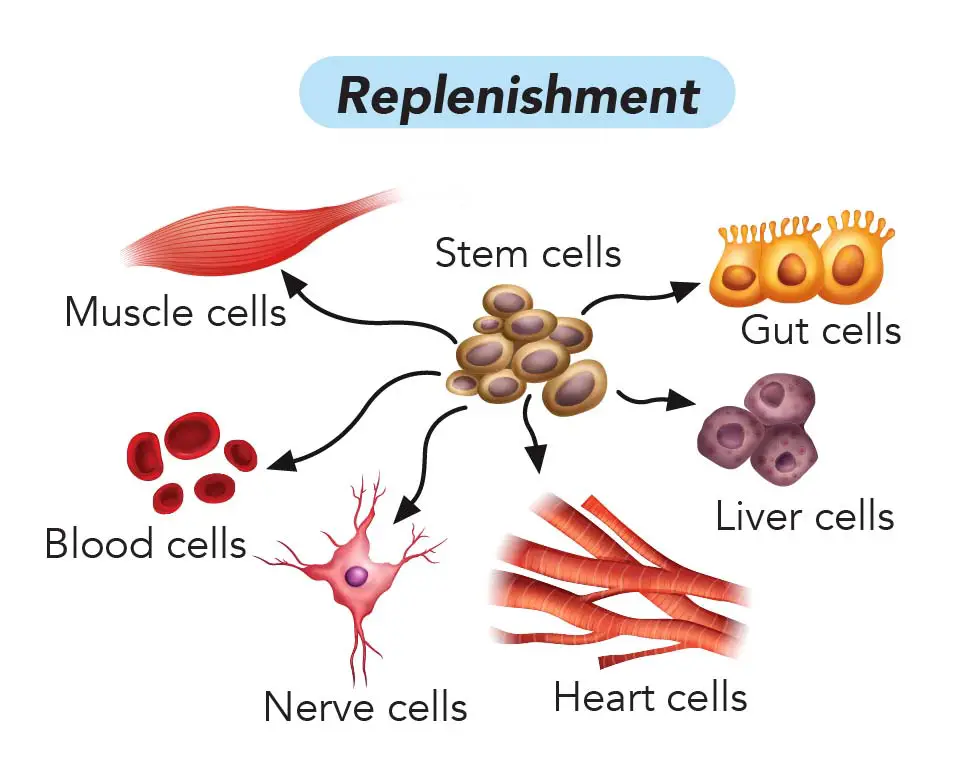 Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
 Cell Division Biology Units Cell Division Cell Cycle
Cell Division Biology Units Cell Division Cell Cycle
 It S Scienterrific Illustration Of Mitosis By D Sayeau Mitosis Teaching Biology Cell Biology
It S Scienterrific Illustration Of Mitosis By D Sayeau Mitosis Teaching Biology Cell Biology
 Characteristics Of Living Organisms Biology Notes For Igcse 2014 Biology Notes Cell Respiration Body Systems
Characteristics Of Living Organisms Biology Notes For Igcse 2014 Biology Notes Cell Respiration Body Systems
 Bacterial Binary Fission The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Article Khan Academy Mitosis Biology Notes Origin Of Replication
Bacterial Binary Fission The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Article Khan Academy Mitosis Biology Notes Origin Of Replication
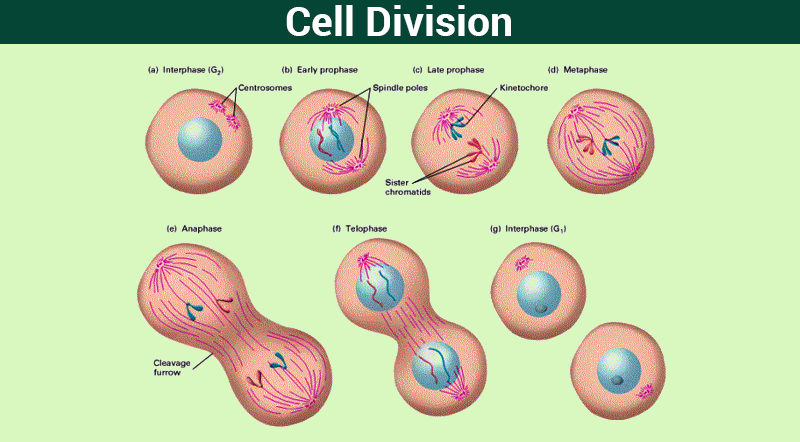 Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis And Different Phases Of Cell Cycle
Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis And Different Phases Of Cell Cycle
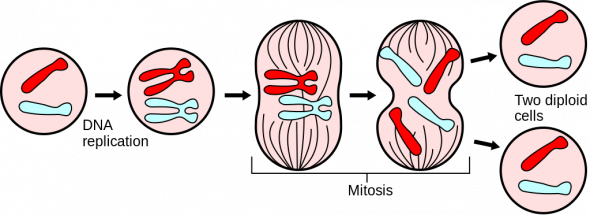 Growth Development And Reproduction Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth
Growth Development And Reproduction Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth
 Cell Growth Division Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
Cell Growth Division Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
 How Does Cell Division Solve The Problem Of Increasing Size Biology Dictionary
How Does Cell Division Solve The Problem Of Increasing Size Biology Dictionary
 Cell Reproduction Mitosis Human Embryo Microscopic
Cell Reproduction Mitosis Human Embryo Microscopic
 Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
 The Epidermal Growth Factor Egf Pathway That Promotes Cell Division Biology Forums Gallery Cell Division Epidermal Growth Factor Cell Growth
The Epidermal Growth Factor Egf Pathway That Promotes Cell Division Biology Forums Gallery Cell Division Epidermal Growth Factor Cell Growth


