Yeast Cell Division Time
Pombe is a popular system for studies of cell growth and division partly because of its regular size. Fission yeast shares numerous features with human chromosomes including large and complex centromeres and replication origins.
 Controlling Cell Size Through Sizer Mechanisms Sciencedirect
Controlling Cell Size Through Sizer Mechanisms Sciencedirect
CLS is the length of time that a non-dividing cell survives.

Yeast cell division time. Yeast cells can only divide around 7 times before their entire surfaces are covered in division scars thereby preventing further cell division. Here we address how the natural variation in replicative lifespan within wild-type populations of yeast cells correlates to three biogenesis-related parameters namely cell size ribosomal protein Rpl13A-GFP levels and division times. In physical appearance the cell wall of old cells becomes somewhat wrinkled in appearance in contrast to a young vigorous cell which has a smooth turgid.
For most mutants cells early in the cell cycle at the time of the tempera- ture shift before the execution point arrest in the first cell cycle while those. Yeasts like all fungi may have asexual and sexual reproductive cycles. The synchronous growth of the cells was started by lowering the temperature to a permissive temperature of 25C.
Sherman Getting started with yeast Methods Enzymol. The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates into the daughter cell. For example in the context of nutrients as a growth-limiting factor yeast cells arrest proliferation mainly in the G 1 phase of the cell cycle.
Fission yeast also have an extremely short generation time 2 to 4 hours which also makes it an easy model system to observe and grow in the laboratory Fission yeasts simplicity in genomic structure yet similarities with mammalian genome ease of ability to manipulate and ability to be used for drug analysis is why fission yeast is making many contributions to biomedicine and cellular biology research and a model system for genetic analysis. Additionally its chromosome structure is a good model for human chromosomes. Its easy and inexpensive to grow fission yeast and manipulate the cells in the laboratory.
Starting point was lee hartwells 1970s landmark papers describing the first cell division cycle cdc mutants in budding yeast these mutants were blocked at different cell cycle stages and so were unable to complete the cell cycle the fission yeast schizosaccharomyces pombe has served as an important model organism for investigating cellular morphogenesis this unicellular rod shaped fission. The mutants were examined by time-lapse photomicroscopy to determine the number of cell cycles completed at the restrictive temperature before arrest. The division cycle is quite rapid with a generation time of S.
2-photon timelapse of FP expressing yeast cell division About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features 2021. In the longer. Chronological lifespan CLS and replicative lifespan RLS.
Lifespan is mainly examined using 2 different concepts. The most common mode of vegetative growth in yeast is asexual reproduction by budding where a small bud also known as a bleb or daughter cell is formed on the parent cell. Lets try to model a dividing yeast population using a demographic model to keep track of how many times each cell has divided.
Since under ideal conditions the yeast cell may duplicate itself within 1½ to 2 hr when vigorously growing the reproductive capacity of these cells can be imagined. Imaging wild type yeast cells in microfluidic devices we observe that in all cells and at all ages the division times as well as the increase in cell size that single yeast undergo while aging negatively correlate to their lifespan. Normal laboratory haploid strains have a doubling time of 90 minutes in YPD medium and 140 minutes in synthetic media during the exponential phase of growth.
The cells were inoculated at 2510 of the final cell concentration in 400 ml YEPD medium containing 2 glucose 2 polypeptone and 1 yeast extract and were precultured at 36C for 2 h SH3009 and for 4 h K164-9 to obtain the arrested cells. It has been found however as cells age the generation time for a particular medium and set of conditions is extended and finally becomes as long as 6 hr per generation. Length of G1 phase.
P15 2nd paragraph PubMed ID 12073320. Pombe between 2 and 4 hours.
How Long Do Yeast Cells Take Before Dividing Quora
 Cell Biology Of Yeast Zygotes From Genesis To Budding Sciencedirect
Cell Biology Of Yeast Zygotes From Genesis To Budding Sciencedirect
 Fission Yeast Cell Cycle Pombenet Forsburg Lab Usc Dana And David Dornsife College Of Letters Arts And Sciences
Fission Yeast Cell Cycle Pombenet Forsburg Lab Usc Dana And David Dornsife College Of Letters Arts And Sciences
 How Fission Yeast Fission In The Middle Cell
How Fission Yeast Fission In The Middle Cell
Illustration Of Cytokinetic Key Events In Different Cell Cycle Phases Download Scientific Diagram
 Measurement Of Mass Density And Volume During The Cell Cycle Of Yeast Pnas
Measurement Of Mass Density And Volume During The Cell Cycle Of Yeast Pnas
 Cell Cycle Inhibitor Whi5 Records Environmental Information To Coordinate Growth And Division In Yeast Sciencedirect
Cell Cycle Inhibitor Whi5 Records Environmental Information To Coordinate Growth And Division In Yeast Sciencedirect
 Yeast Propagation And Maintenance Principles And Practices Maltose Falcons
Yeast Propagation And Maintenance Principles And Practices Maltose Falcons
 Building Blocks Are Synthesized On Demand During The Yeast Cell Cycle Pnas
Building Blocks Are Synthesized On Demand During The Yeast Cell Cycle Pnas
How Long Do The Different Stages Of The Cell Cycle Take
 Budding Yeast Cell Progression Through The Cell Cycle Download Scientific Diagram
Budding Yeast Cell Progression Through The Cell Cycle Download Scientific Diagram
 The Growth Phase Cycle For W303 Yeast Cells Based On The Od 660nm Download Scientific Diagram
The Growth Phase Cycle For W303 Yeast Cells Based On The Od 660nm Download Scientific Diagram
 Budding Yeast For Budding Geneticists A Primer On The Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Model System Genetics
Budding Yeast For Budding Geneticists A Primer On The Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Model System Genetics
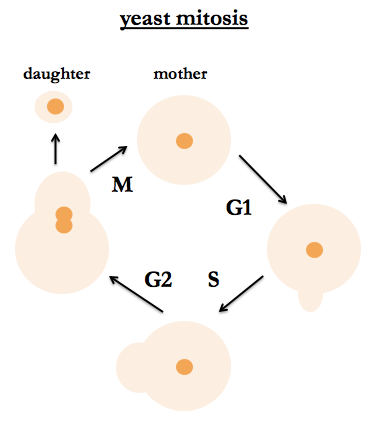 Genetics 02 Introduction To Yeast Genetics And Complementation
Genetics 02 Introduction To Yeast Genetics And Complementation
 Yeast Cell Division And Bud Scar Formation A The Budding Of Each Download Scientific Diagram
Yeast Cell Division And Bud Scar Formation A The Budding Of Each Download Scientific Diagram
 Logic Of The Yeast Metabolic Cycle Temporal Compartmentalization Of Cellular Processes Science
Logic Of The Yeast Metabolic Cycle Temporal Compartmentalization Of Cellular Processes Science
 Yeast As A Model Organism For Studying Cancer Learn Science At Scitable
Yeast As A Model Organism For Studying Cancer Learn Science At Scitable
 Meiotic Divisions Are Conserved Between Yeast And Higher Eukaryotes Download Scientific Diagram
Meiotic Divisions Are Conserved Between Yeast And Higher Eukaryotes Download Scientific Diagram
