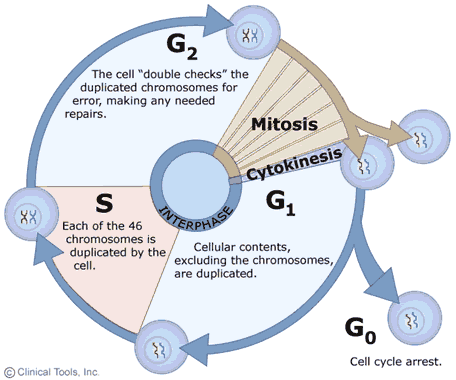
Tumors Resulting From The Loss Of Control Of Cell Division
The daughter cells resulting in mitotic cell division are genetically identical. The DTs are significantly correlated with the histological type.
Diagrams Cell Cycle Cell Division By Mitosis Meiosis Sexual Reproduction Haploid Diploid Chromosome Numbers Zygote Gametes Sperm Eggs Binary Fission Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Percentile Growth Charts Graphs Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology Revision Notes
Its either histines or kinetochoreim betting on histones actually its cancer the person above is.

Tumors resulting from the loss of control of cell division. Consequently this impairs APC capacity of antigen presentation and T. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments demonstrate that tumor STC1 supports tumor progression and enables tumor resistance to checkpoint blockade in murine tumor models. Regulation of cell cycle.
Facebook Twitter Create an Account Sign In. So if the cell is damaged or unhealthy in any way the cell cycle prevents division from taking place. Cell division can be harmful to the body when it gets out of control.
The goal of the cell cycle is to produce two viable healthy daughter cells. This is the currently selected item. Tumors serve no physiological functionTumors can be safe benign or badIt is caused by uncontrolled cell division.
Cancer is unchecked cell growth. When the cycle proceeds without control cells can divide without order and accumulate genetic defects that can lead to a cancerous tumor. The p53 gene that normally inhibits the growth of tumours resulting in inability to stop uncontrolled cell division.
Mutations in genes can cause cancer by accelerating cell division rates or inhibiting normal controls on the system such as cell cycle arrest or programmed cell. Regulation of cell cycle. New growth tumor Benign Tumor.
Tumors frequently have decreased cell death as a primary mode of increased cell proliferation. Cancer results from a disruption of the normal regulation of the cell cycle. The most common and best-known example of this is cancer when rapid and uncontrolled cell division creates tumors in the body.
Substantial increase in the rate of cell division - sometimes signals a loss of control over cell division. Tumors resulting from the loss of control of cell division. A mutation results in the production of an abnormal protein or enzyme a mutation occurs near or around the proto-oncogene turning on cell division when not required a mutation occurs near or around tumour suppressor gene eg.
Regulation of cell cycle. Terms in this set 36 Hyperplasia. -remain in one place in a single well defined mass.
Tumors resulting from the loss of control of cell division. They depend upon 1 the duration of the cell cycle whose mean duration is 2 days with small variations from tumor to tumor 2 the proportion of proliferating cells and consequently the cell birth rate which varies widely among tumors and which is significantly correlated to the DT. Many of the gene products which appear to control apoptotic tendencies are regulators of cell cycle progression.
Loss of cell cycle control in cancer. It does this through three checkpoints throughout. Genetic changes resulting in loss of programmed cell death apoptosis are likely to be critical components of tumorigenesis.
False The tumor shown in the figure above is most likely malignant. Mechanistically tumor STC1 interacts with calreticulin CRT an eat-me signal and minimizes CRT membrane exposure thereby abrogating membrane CRT-directed phagocytosis by antigen-presenting cells APCs including macrophages and dendritic cells. When hyperplasia develops signaling a loss of control of cell division it always results in cancer.
Cancer and the cell cycle. How microtubules control the positioning of the cell division plane is the subject of much controversy. The results show that the DT of human tumor varies widely from less than one week to over one year with a median value of approximately 2 months.
How cancer can be linked to overactive positive cell cycle regulators oncogenes or inactive negative regulators tumor suppressors. In current models microtubules either promote furrowing at the cell equator by means of the. The cell cycle also provides time for the cell to perform quality control on all of the cellular components to make sure the cell is healthy enough to divide.
Loss of cell cycle control in cancer.
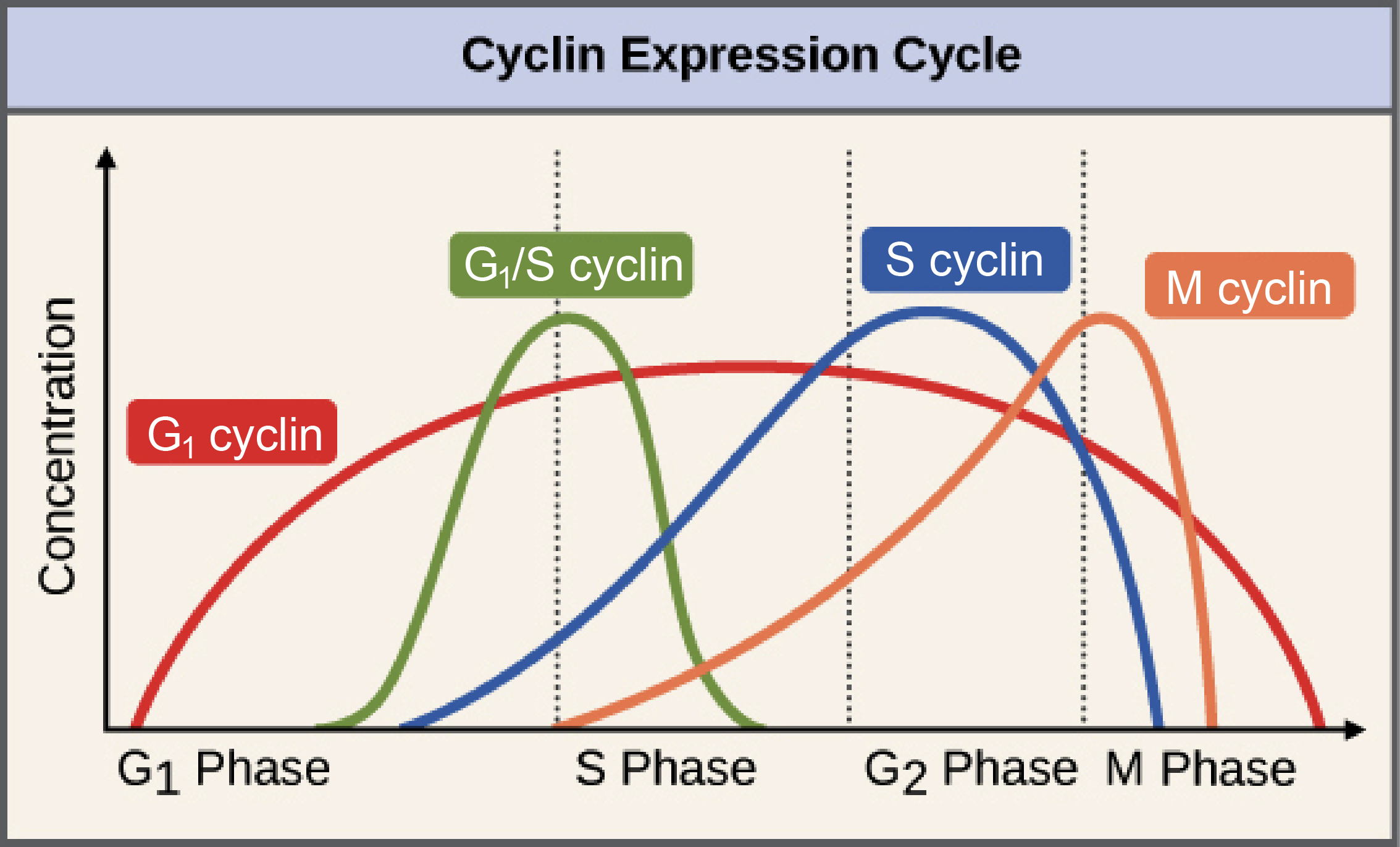 Cell Cycle Regulators Article Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Regulators Article Khan Academy
 Control Of The Cell Cycle Biology I
Control Of The Cell Cycle Biology I
 The Cell Cycle Boundless Biology
The Cell Cycle Boundless Biology
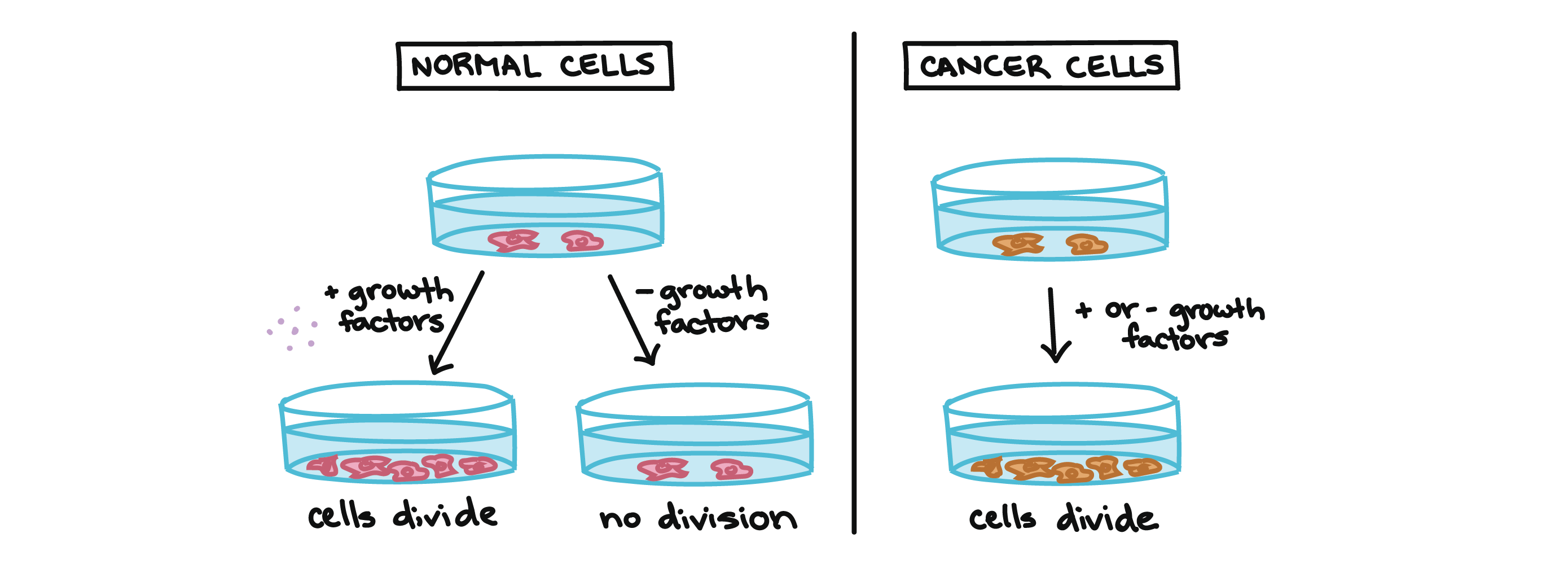 Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
The Cell Cycle Chapter 16 Pages 650 661 669 677 Having Examined Some Of The Ways In Which Cells Communicate With Each Other We Start Now To Look At That Most Fundamental And Mysterious Process Cell Division All Cells Must Divide At Some Point In
 Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology I
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology I
6 3 Cancer And The Cell Cycle Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition Molnar
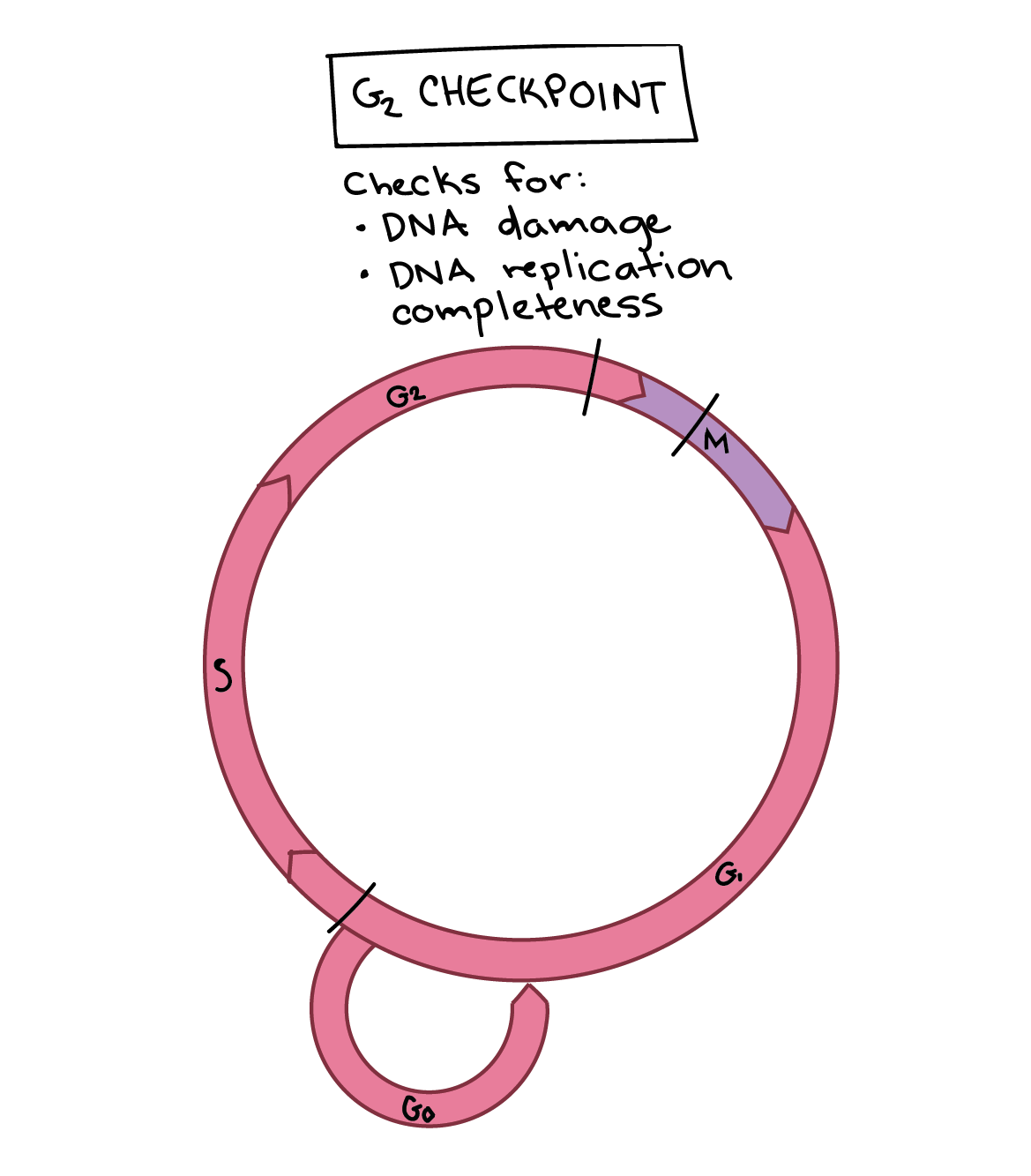 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
 Quia 9ap Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Detailed
Quia 9ap Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Detailed
 1 The Cell Cycle Is Divided Into Four Phases G 1 S G 2 M Resting Cells Are In A G 0 Phase Out Of The Cycle Che Cell Cycle Science Cells Science Notes
1 The Cell Cycle Is Divided Into Four Phases G 1 S G 2 M Resting Cells Are In A G 0 Phase Out Of The Cycle Che Cell Cycle Science Cells Science Notes
 Cell Cycle Diagram The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Cells That Are Destined To Divide Progress Cell Cycle Cell Biology Eukaryotic Cell
Cell Cycle Diagram The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Cells That Are Destined To Divide Progress Cell Cycle Cell Biology Eukaryotic Cell
 The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To Stop The Growth Of Cancer Cells Cyclacel
The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To Stop The Growth Of Cancer Cells Cyclacel
 Fundamental Processes Overview Of The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle Mitosis
Fundamental Processes Overview Of The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle Mitosis
 7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
 Cell Cycle Arrest An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cell Cycle Arrest An Overview Sciencedirect Topics