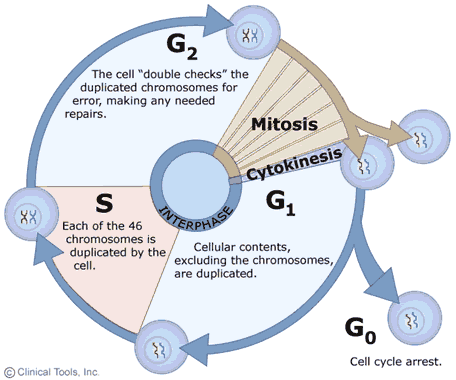
The Cell Cycle Controls Cell Division Only In
Cancer is the result of unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
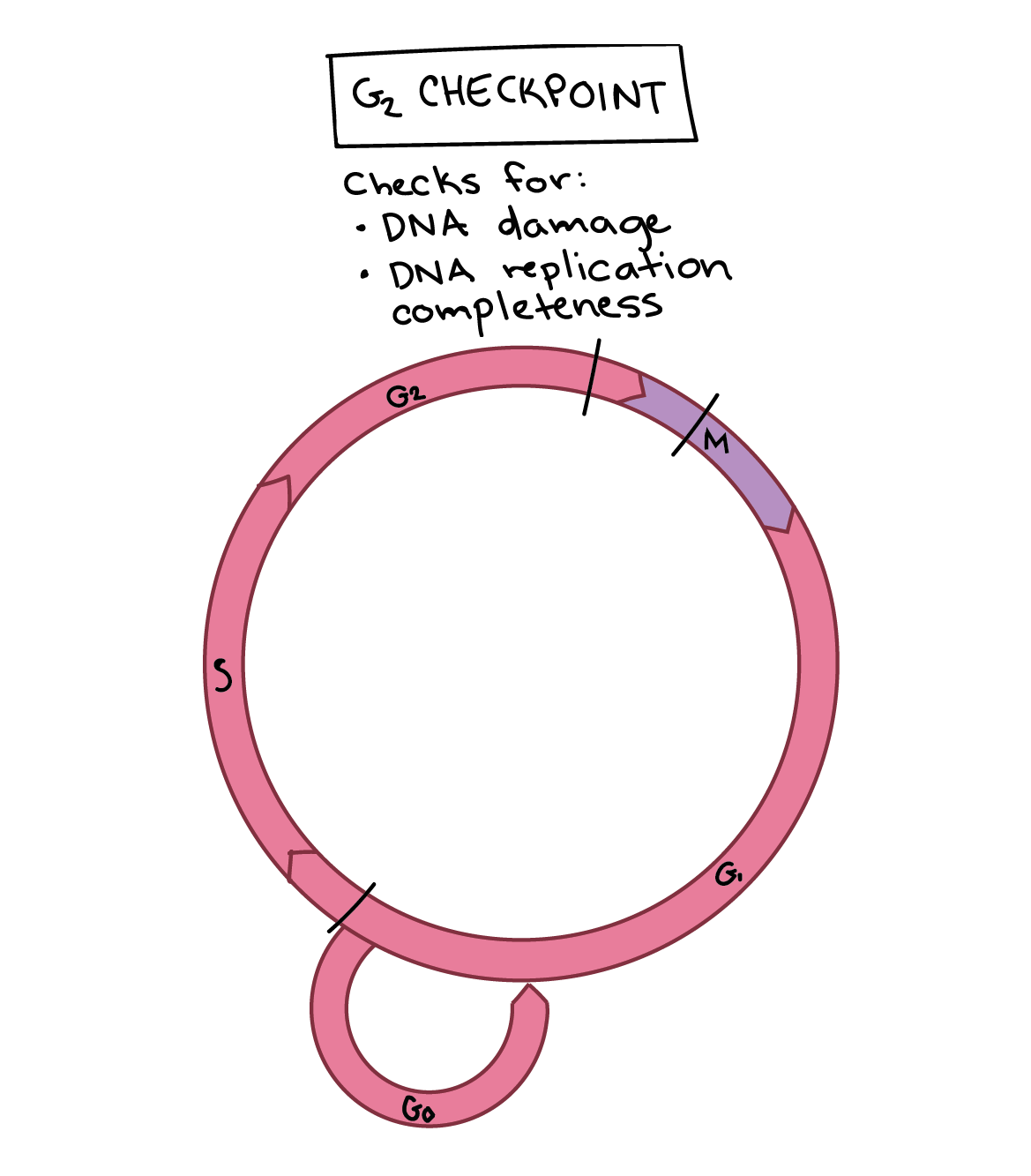 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
The proteins phosphorylated by Cdks are involved in advancing the cell to the next.

The cell cycle controls cell division only in. In cell biology mitosis is a part of the cell cycle. A system that controls the cycling of the cycle and ensures the cell only enters the next phase when passage through the previous one is complete. Each successive cell division will give rise to daughter cells.
1E which would occur predominantly through dilution due to cell division 23 24 as PU1s protein half-life is substantially longer than the progenitor cell-cycle length. The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. Cell controls on division Contact with other cells Once DNA cell directions is copied cell divides Sequence of steps - one cant happen before the previous one end.
Why do Cells divide. Mistakes in the duplication or distribution of the chromosomes lead to mutations that may be passed forward to every new cell produced from the abnormal cell. Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
Describe the relationship between growth factors cyclin and CDKs. How is the Cell Cycle Controlled in Normal Cells Cell Cycle Control through Checkpoints. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Cyclins Cytokinesis Interphase Mitotic Phase.
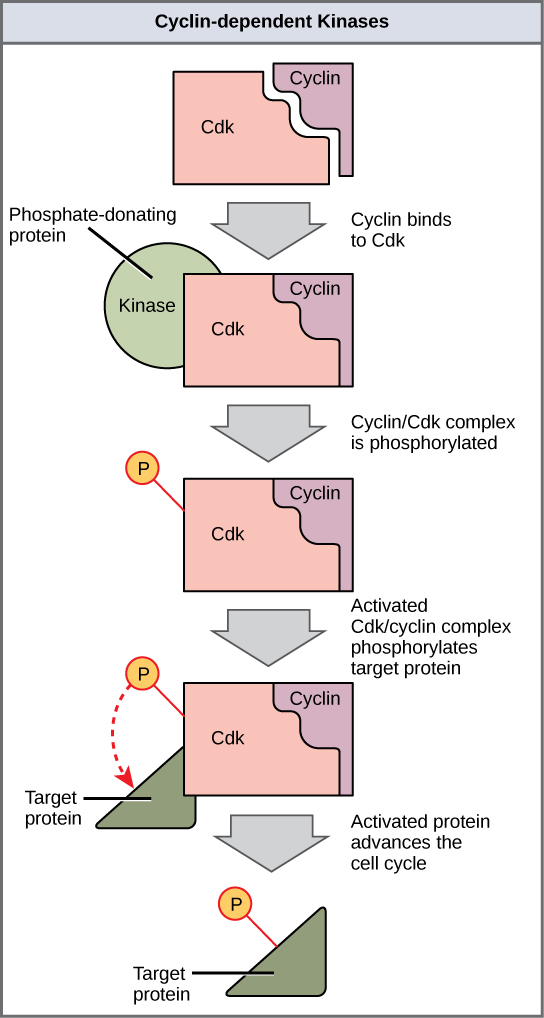
They control the synthesis of cyclin which regulate the activity of CDKs which activate DNA replication. Like all kinases Cdks are enzymes kinases that phosphorylate other proteins. What is Cell Cycle.
Cyclin is produced 4. Changes that take place in cells as they change -Develop specifics shapes. A vegetative division whereby each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell and a reproductive cell division whereby the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is reduced by half to produce haploid gametes.
Cell cycle is the series of events the take place within the cell leading to the division of the cell into two identical daughter cells. Cyclin binds to. These events include the duplication of its DNA DNA replication and some of its organelles and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Here we review how deregulated cell cycle control contributes to increased proliferation in AML and favors genomic instability a prerequisite to confer selective advantages to particular clones in order to adapt and independently proliferate in the presence of a changing microenvironment. Growth factors bind to growth factor receptors 2. S Phase-Synthesis-Longest 10-12 hrs-DNA is.
Mutants carrying lesions in three genes that control the cell-division cycle are described. Cells carrying the cdc-1 mutation terminate at the execution point most cells ending up with a tiny bud that does not develop further. We discuss the connection between differentiation and proliferation with regard to leukemogenesis and.
Result of cells producing new cells through cell division. Control of the Cdc2 kinase by inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation was indicated by high phosphotyrosine in the inactive enzyme of arrested pith and. Faulty instructions lead to a protein that does not function normally.
To prevent a compromised cell from continuing to divide there are internal control mechanisms that operate at three main cell cycle. Growth Development Repair and Reproduction. All three genes cdc-1 cdc-2 and cdc-3 execute early in the cell cycle at about the time of bud initiation but differ in their termination points.
In eukaryotes there are two distinct types of cell division. A control system that initiates and. This produces proteins that allow cyclin mRNA to be transcribes and translated 3.
Plumbaginifolia Viv cytokinin kinetin was stringently required only in late G2 phase of the cell division cycle cdc and cells lacking kinetin arrested in G2 phase with inactive p34cdc2-like H1 histone kinase. Terms in this set 38 Cell Cycle-Involves DNA replication dividing to create 2 identical daughter cells -Control levels---Protein phosphorylation that moves that cell from one stage to the next---Checkpoint controls. Also that the phases of the cell cycle are entered in the correct order.
Phosphorylation activates the protein by changing its shape. Satisfactory passage through all four phases and usually the various checkpoints of the cell cycle are critical for cell division QC. How do growth factors control cell division.
Changes in PU1 levels during B-cell or macrophage differentiation may result from changes in either the rate of PU1 synthesis or the rate of PU1 removal Fig. Control of the Cell Cycle It is essential that daughter cells be exact duplicates of the parent cell. To be fully active the Cdkcyclin complex must also be phosphorylated in specific locations.
Cell-Cycle Control Cell Division. The loss of cell cycle control begins with a DNA sequence change of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory molecules known as a mutation. Cyclins regulate the cell cycle only when they are tightly bound to Cdks.
 Quia 9ap Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Detailed
Quia 9ap Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Detailed
 Control Of The Cell Cycle Biology I
Control Of The Cell Cycle Biology I
 Fundamental Processes Overview Of The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle Mitosis
Fundamental Processes Overview Of The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cycle Mitosis
 The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To Stop The Growth Of Cancer Cells Cyclacel
The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To Stop The Growth Of Cancer Cells Cyclacel
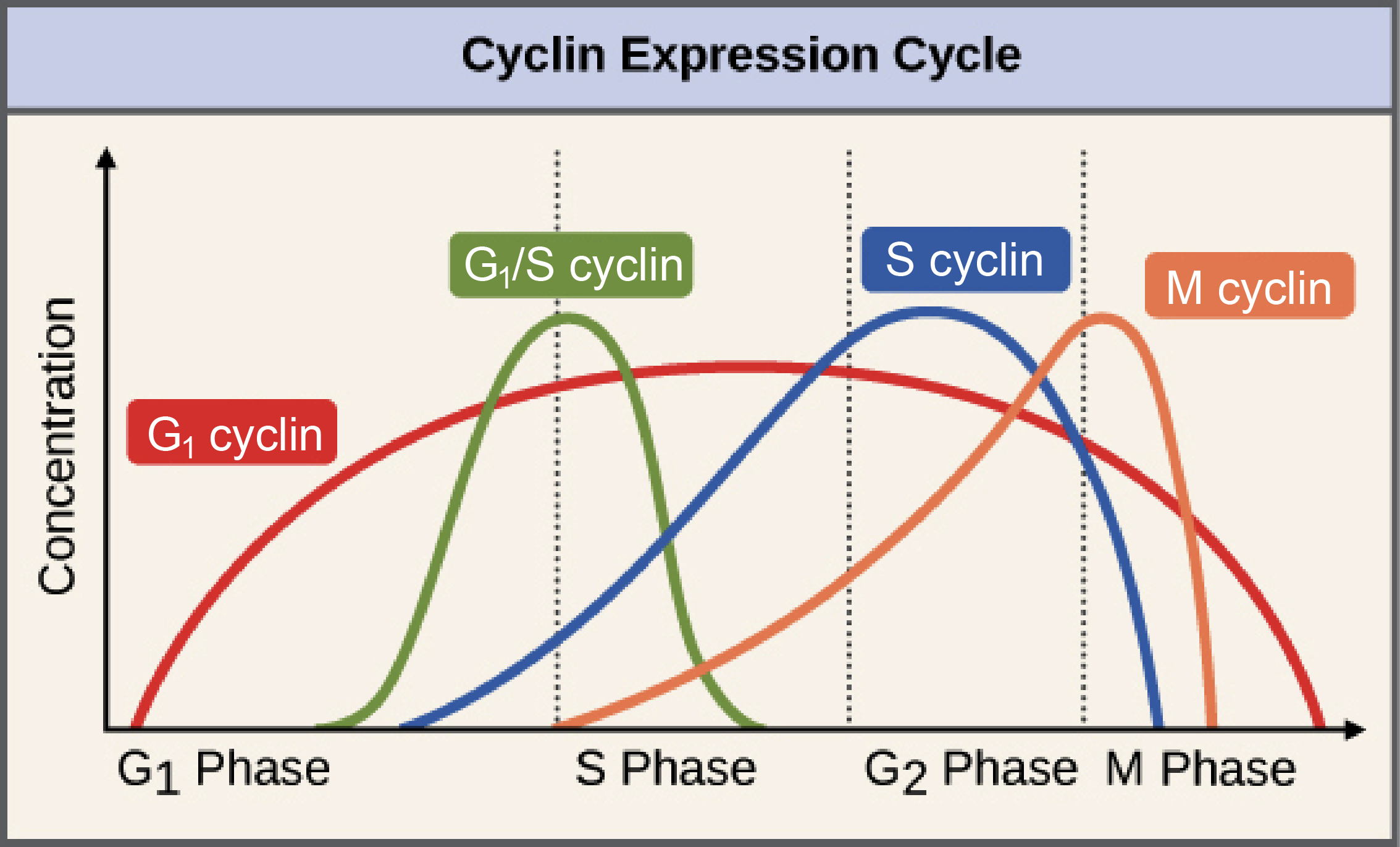 Cell Cycle Regulators Article Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Regulators Article Khan Academy
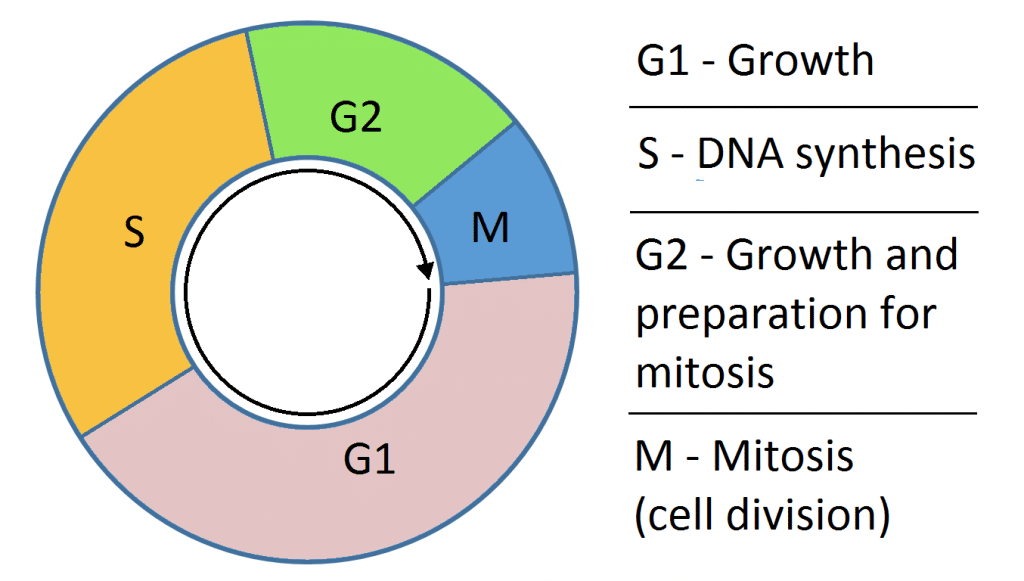 The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
 Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
Cell Division Binary Fission And Mitosis
 10 3b Regulation Of The Cell Cycle At Internal Checkpoints Biology Libretexts
10 3b Regulation Of The Cell Cycle At Internal Checkpoints Biology Libretexts
 Cell Cycle Control Video Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Control Video Khan Academy
 Cell Cycle Domino Model Clock Model Learn Science At Scitable
Cell Cycle Domino Model Clock Model Learn Science At Scitable
Diagrams Cell Cycle Cell Division By Mitosis Meiosis Sexual Reproduction Haploid Diploid Chromosome Numbers Zygote Gametes Sperm Eggs Binary Fission Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Percentile Growth Charts Graphs Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology Revision Notes
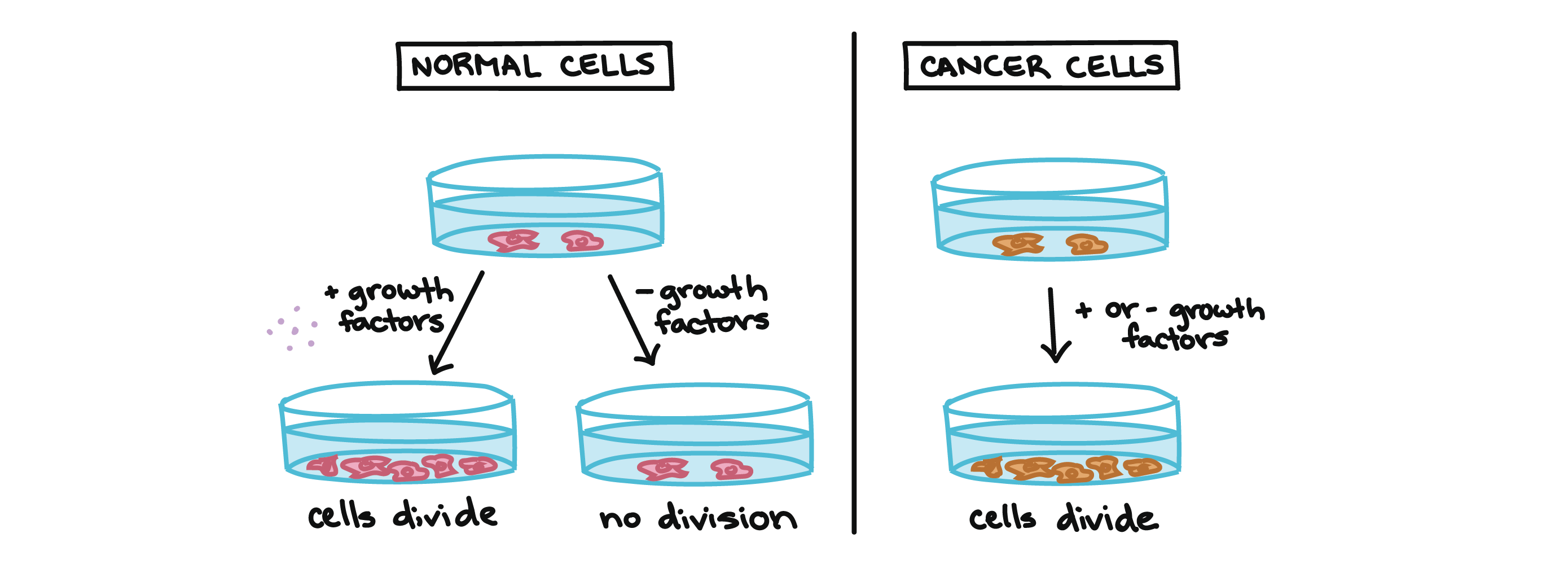 Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
19 3 Regulation Of The Cell Cycle Biology Libretexts
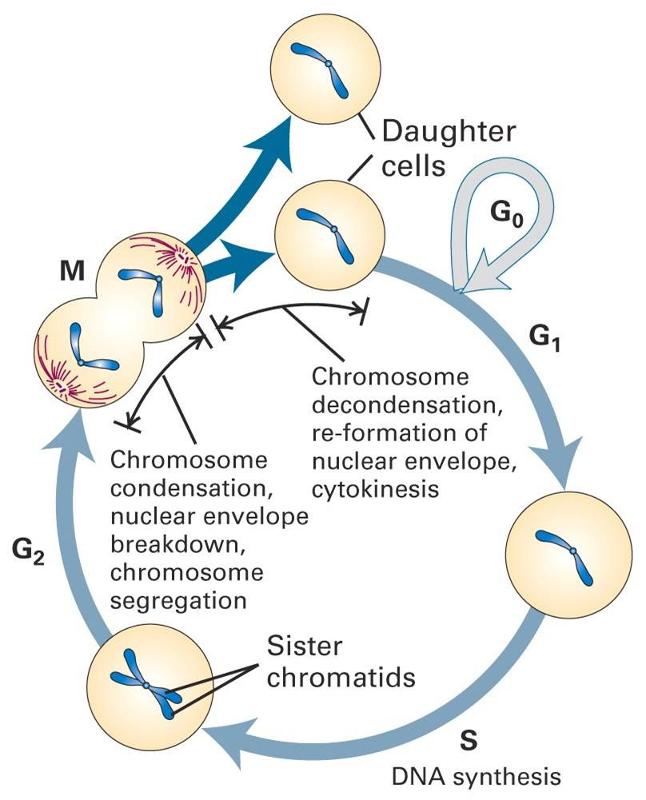 Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
 7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
7 2 Cell Cycle And Cell Division Biology Libretexts
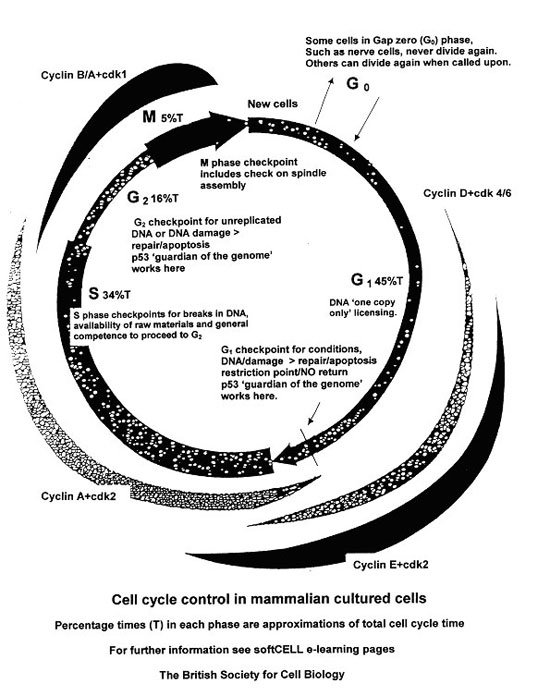 Cell Cycle Control British Society For Cell Biology
Cell Cycle Control British Society For Cell Biology
 1 The Cell Cycle Is Divided Into Four Phases G 1 S G 2 M Resting Cells Are In A G 0 Phase Out Of The Cycle Che Cell Cycle Science Cells Science Notes
1 The Cell Cycle Is Divided Into Four Phases G 1 S G 2 M Resting Cells Are In A G 0 Phase Out Of The Cycle Che Cell Cycle Science Cells Science Notes