Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Stem Cell Division
Notably stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells. In the symmetric division model a stem cell produces two differentiated cells or two stem cells.
 Orientation Of The Mitotic Spindle Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Divisions Download Scientific Diagram
Orientation Of The Mitotic Spindle Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Divisions Download Scientific Diagram
We compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric and mixed stem cell divisions and focus on the rate at which double-hit mutants are generated.

Symmetric vs asymmetric stem cell division. It turns out that symmetrically-dividing cells generate such mutants at a rate which is significantly lower than that of asymmetrically-dividing cells. This result holds whether single-hit intermediate mutants are disadvantageous neutral or advantageous. It turns out that symmetrically-dividing cells generate such mutants at a rate which is significantly lower than that of asymmetrically-dividing cells.
Alternatively they can orient their division plane so that only one of the two daughter cells. It is also independent on whether the carcinogenic double-hit mutants are. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise to daughter cells of equivalent fates.
The proper choice of a stem cell to divide asymmetrically or symmetrically has great consequences for development and disease. It is also independent on whether the carcinogenic double-hit mutants are produced only. The facultative use of symmetric or.
In the asymmetric division model a stem cell produces one differentiated cell and one stem cell. In contrast to symmetric divisions where self-renewal and differentiation are decoupled asymmetric divisions result in fixed ratios of differentiation and self-renewal incapable of replenishing the stem cell pool upon injury. This result holds whether single-hit intermediate mutants are disadvantageous neutral or advantageous.
It is also independent on whether the carcinogenic double-hit mutants are produced only. The modes of stem cell division asymmetric vs. In the symmetric division model a stem cell produces.
Thus asymmetric division is not necessary for stem-cell identity but rather is a tool that stem cells can use to maintain appropriate numbers of progeny. It turns out that symmetrically-dividing cells generate such mutants at a rate which is significantly lower than that of asymmetrically-dividing cells. One copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate.
It turns out that symmetrically-dividing cells generate such mutants at a rate which is significantly lower than that of asymmetrically-dividing cells. We compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric and mixed stem cell divisions and focus on the rate at which double-hit mutants are generated. The key difference between symmetric and asymmetric stem cell division is that symmetric stem cell division produces two differentiated cells or two stem cells with equal cell fates while asymmetric stem cell division produces one stem and one non-stem daughter cell which have different fates.
In the asymmetric division model a stem cell produces one differentiated cell and one stem cell. The number of divisions required to maintain the stem cell pool for extended periods is lower using population asymmetry compared to asymmetric cell division possibly lowering replicative aging and somatic mutations. In the symmetric division model a stem cell produces two differentiated cells or two stem cells.
Symmetric and asymmetric stem cell divisions. It is also independent on whether the carcinogenic double-hit mutants are produced only. An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates.
Symmetric are tightly regulated during development and regeneration. To achieve this remarkable task they can undergo an intrinsically asymmetric cell division whereby they segregate cell fate determinants into only one of the two daughter cells. We compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric and mixed stem cell divisions and focus on the rate at which double-hit mutants are generated.
Stem cells self-renew but also give rise to daughter cells that are committed to lineage-specific differentiation. In the asymmetric division model a stem cell produces one differentiated cell and one stem cell. Symmetric and asymmetric stem cell divisions.
This result holds whether single-hit intermediate mutants are disadvantageous neutral or advantageous. This result holds whether single-hit intermediate mutants are disadvantageous neutral or advantageous. New insights have been added to identification behavior and cellular properties of embryonic and tissue-specific stem cells over the last few years.
We compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric and mixed stem cell divisions and focus on the rate at which double-hit mutants are generated.
 Symmetric Stem Cell Division At The Heart Of Adult Neurogenesis Sciencedirect
Symmetric Stem Cell Division At The Heart Of Adult Neurogenesis Sciencedirect
 Asymmetric Division Promotes Therapeutic Resistance In Glioblastoma Stem Cells Biorxiv
Asymmetric Division Promotes Therapeutic Resistance In Glioblastoma Stem Cells Biorxiv
 Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
 Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Divisions In The Asymmetric Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Divisions In The Asymmetric Download Scientific Diagram
 Cell Polarity And Cancer Cell And Tissue Polarity As A Non Canonical Tumor Suppressor Journal Of Cell Science
Cell Polarity And Cancer Cell And Tissue Polarity As A Non Canonical Tumor Suppressor Journal Of Cell Science
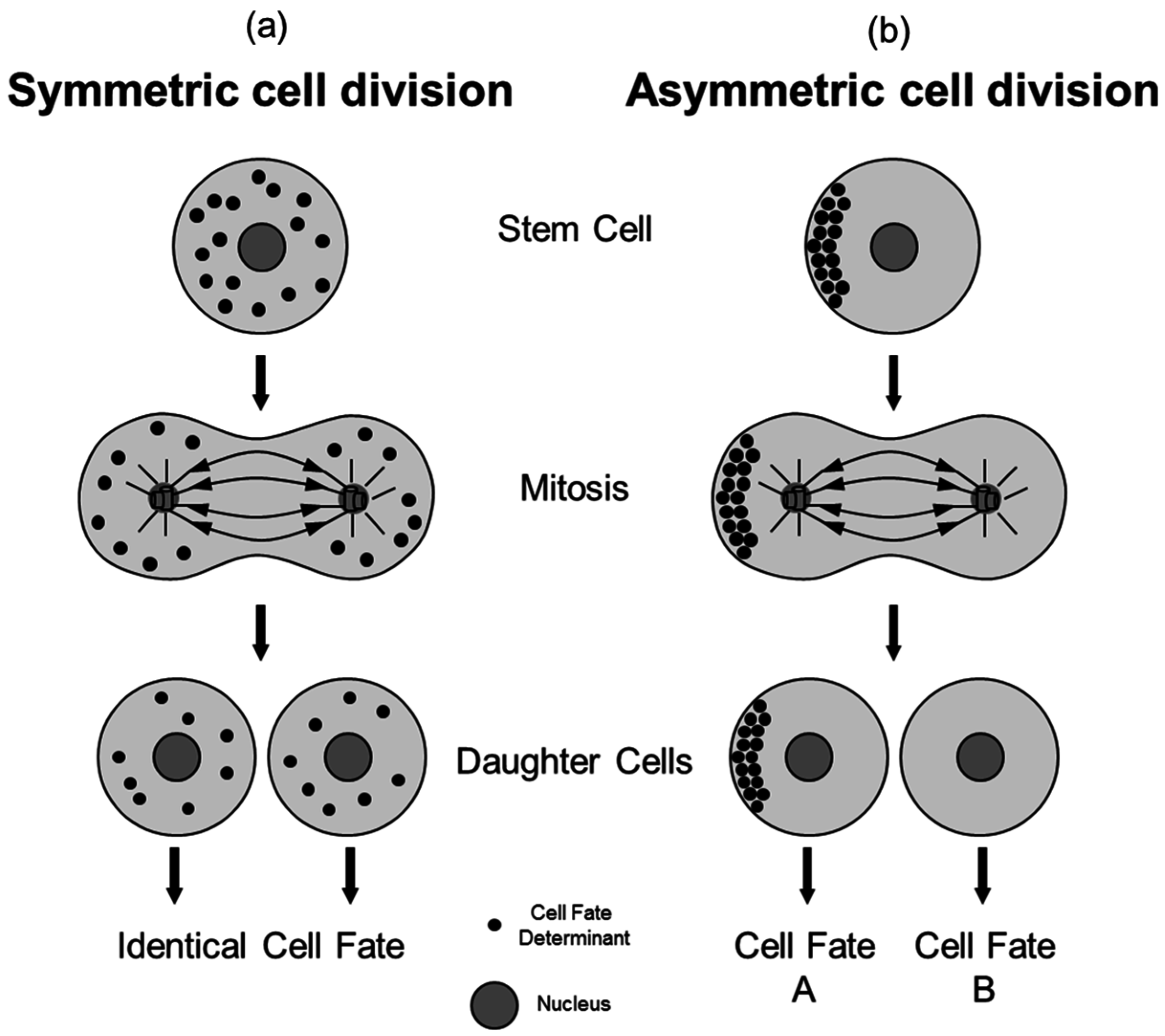 Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html
Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html
 Fearful Symmetry Subversion Of Asymmetric Division In Cancer Development And Progression Cancer Research
Fearful Symmetry Subversion Of Asymmetric Division In Cancer Development And Progression Cancer Research
 Lessons From Development A Role For Asymmetric Stem Cell Division In Cancer Sciencedirect
Lessons From Development A Role For Asymmetric Stem Cell Division In Cancer Sciencedirect
Plos Computational Biology The Role Of Symmetric Stem Cell Divisions In Tissue Homeostasis
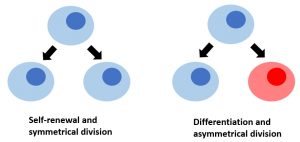 4 2 Overview Of Stem Cells And Their Potential As A Therapeutic Selected Topics In Health And Disease
4 2 Overview Of Stem Cells And Their Potential As A Therapeutic Selected Topics In Health And Disease
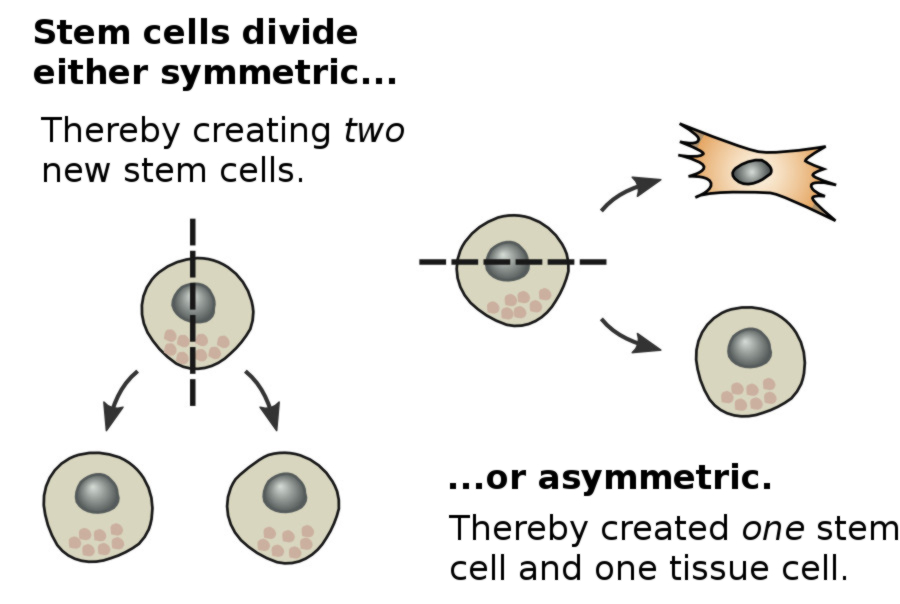 What Are Stem Cells Medical And Scientific Facts
What Are Stem Cells Medical And Scientific Facts
 Differentiation And Asymmetric Divison Ppt Download
Differentiation And Asymmetric Divison Ppt Download
 Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Division Of Adult Stem Cells Determines The Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Division Of Adult Stem Cells Determines The Download Scientific Diagram
 Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division And Maintenance Of Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division And Maintenance Of Download Scientific Diagram
 Dynamics Of Asymmetric And Symmetric Divisions Of Muscle Stem Cells In Vivo And On Artificial Niches Sciencedirect
Dynamics Of Asymmetric And Symmetric Divisions Of Muscle Stem Cells In Vivo And On Artificial Niches Sciencedirect
 Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Download Scientific Diagram
 1 Two Types Of Cell Division Can Occur In Stem Cells The Stem Cells Download Scientific Diagram
1 Two Types Of Cell Division Can Occur In Stem Cells The Stem Cells Download Scientific Diagram
 Modes Of Satellite Stem Cell Division Satellite Stem Cells Can Download Scientific Diagram
Modes Of Satellite Stem Cell Division Satellite Stem Cells Can Download Scientific Diagram
 Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Cell Division In Epithelial Cells Schematic Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Cell Division In Epithelial Cells Schematic Download Scientific Diagram