Regions Of Active Cell Division In Plants Are Called
The transformation of diploid mother cells undergoes a specialized cell. There germ line cells mature with time and some are transformed into gamete producing cells and undergo meiosis and generate haploid cells which are transformed into sperms in males and eggs in females.
 Cell Elongation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cell Elongation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Therefore cell division in the meristem is required to provide new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and initiation of new organs providing the basic structure of the plant body.

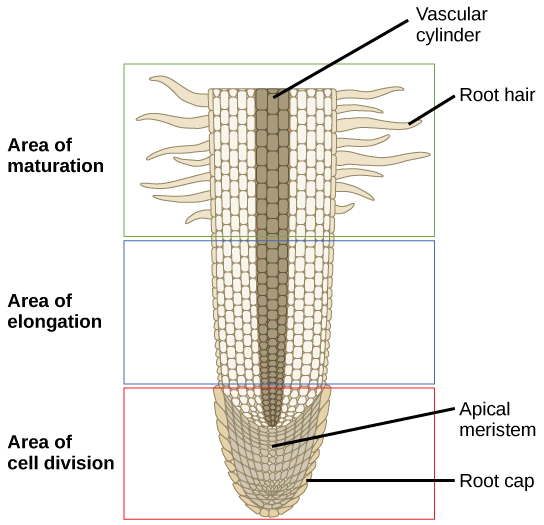
Regions of active cell division in plants are called. The mechanical support and additional conductive pathways needed by increased bulk are provided by the enlargement of the older parts of the shoot and root axes. Growth that occurs from the formation of new cells at the tip of a plant is called primary growth. At the tips of stems and roots.
A cylinder one cell thick that forms the boundary between the cortex and the stele. The region of differentiation and tissue maturation that follows is where the cells. Cell division in eukaryote is much more complicated than prokaryote.
Plant development - Plant development - The activity of meristems. The innermost layer of the cortex in plant roots. Find an answer to your question what is the name given to the specialised regions of active cell division in the plant.
There is a cap of non-reproducing cells that a. The vegetative cell division which produces genetically identical two daughter cells is called mitosis. Im not certain for all plants but I would imagine the onion is a pretty typical plant.
The zone of cell division is closest to the root tip and is made up of the actively-dividing cells of the root meristem which contains the undifferentiated cells of the germinating plant. The amitotic or mitotic cell division is more atypical and diverse in the various groups of organisms such as protists namely diatoms dinoflagellates etc and fungi. A primitive form of cell division is also found which is called amitosis.
The region of cell division includes the apical meristem and the primary meristemsthe protoderm ground meristem and procambiumderived from the apical meristem. Depending upon chromosomal number reduced or not. Characteristically vascular plants grow and develop through the activity of organ-forming regions the growing points.
Vegetative cell division and reproductive cell division. Root area between the stele and epidermis. Meristems can be found.
Growth that causes a plant to increase in width is called secondary growth. These gametes are produced only in specialized structures called reproductive organs such as gonads and testicles in higher animals ovary-ovules and stamens-anthers in angiosperm plants both are specialized organs. Eukaryotic cell divisions can be classified as Mitosis equational division and Meiosis reductional division.
In onion roots its the tip. A zone of cell division a zone of elongation and a zone of maturation. These regions starting at the tip and moving upwards towards the stem are the root cap zone of active cell division zone of cell elongation and zone of maturation.
The zone of elongation is where the newly-formed cells increase in length thereby lengthening the root. The first two are compacted in the first centimeter or less of the axis with the latter two no more than 45 centimeters from the tip. Regions of active cell division in plants are called.
Plants grow at the tips of roots and stems in regions of active cell division called meristem. The lengthening of plant roots and shoots is called. Beginning at the first root hair is the zone of cell maturation where the root.
Cell division both in plants and animal cells can be divided into two types. The root tip can be divided into three zones. Plants grow in regions of active cell division called.
Meristematic cells are analogous in function to stem cells in animals are incompletely or not at all differentiated and are capable of continued cellular division youthful. The zone of primary growth in roots where cells complete their differentiation and become functionally mature. As is generally true of nonmeristematic regions elsewhere in the plant body root length in the second region is increased as a result of cell elongation rather than by cell division.
 Mitosis And Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key Meiosis Mathematics Worksheets Mitosis
Mitosis And Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key Meiosis Mathematics Worksheets Mitosis
 Cell Division In A Frog Zygote Fertilised Egg Educationalgifs Cell Division Teaching Biology Eggs
Cell Division In A Frog Zygote Fertilised Egg Educationalgifs Cell Division Teaching Biology Eggs
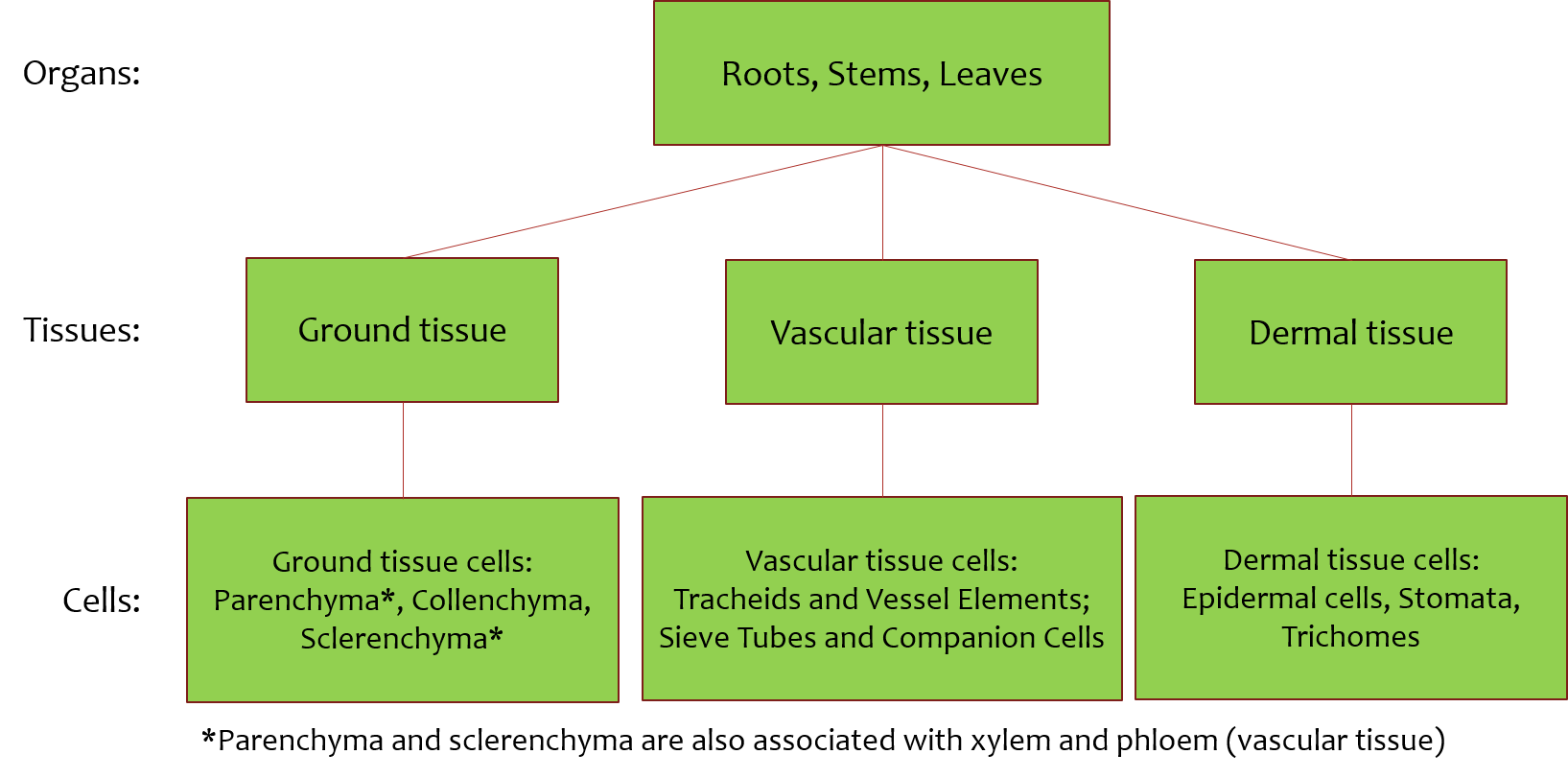 Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology
Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology
 Figure 11 28 Infection By Ti Plasmid In The Process Of Causing Crown Gall Disease The Bacterium Agrobacterium Tumefacie Plants Genetic Engineering Plant Cell
Figure 11 28 Infection By Ti Plasmid In The Process Of Causing Crown Gall Disease The Bacterium Agrobacterium Tumefacie Plants Genetic Engineering Plant Cell
6 2 The Cell Cycle Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
 Gr2 Jpg 513 287 Plant Science Science Transcription
Gr2 Jpg 513 287 Plant Science Science Transcription
 Sempeverium Tectorum Notice Something A Bit Unique About This One It S What Is Known As Crested A Bit Of A Rarity To Enjoy Here S A Bit Of A Mor With Images
Sempeverium Tectorum Notice Something A Bit Unique About This One It S What Is Known As Crested A Bit Of A Rarity To Enjoy Here S A Bit Of A Mor With Images
 The Cell Cycle Boundless Biology
The Cell Cycle Boundless Biology
 Difference Between Plant Cell And Bacterial Cell Definition Characteristics Role Similarities And Differences Exocrine Gland Endocrine Endocrine System
Difference Between Plant Cell And Bacterial Cell Definition Characteristics Role Similarities And Differences Exocrine Gland Endocrine Endocrine System
 The Root Transition Zone A Hot Spot For Signal Crosstalk Trends In Plant Science
The Root Transition Zone A Hot Spot For Signal Crosstalk Trends In Plant Science
 Medical Medical Plant Tissue Biology
Medical Medical Plant Tissue Biology
 Apical Meristem Definition Development Facts Britannica
Apical Meristem Definition Development Facts Britannica
 Image Result For Cofactors And Coenzymes Biochemistry Image
Image Result For Cofactors And Coenzymes Biochemistry Image
 Plant Development Ii Primary And Secondary Growth Organismal Biology
Plant Development Ii Primary And Secondary Growth Organismal Biology
 Plant Development Boundless Biology
Plant Development Boundless Biology