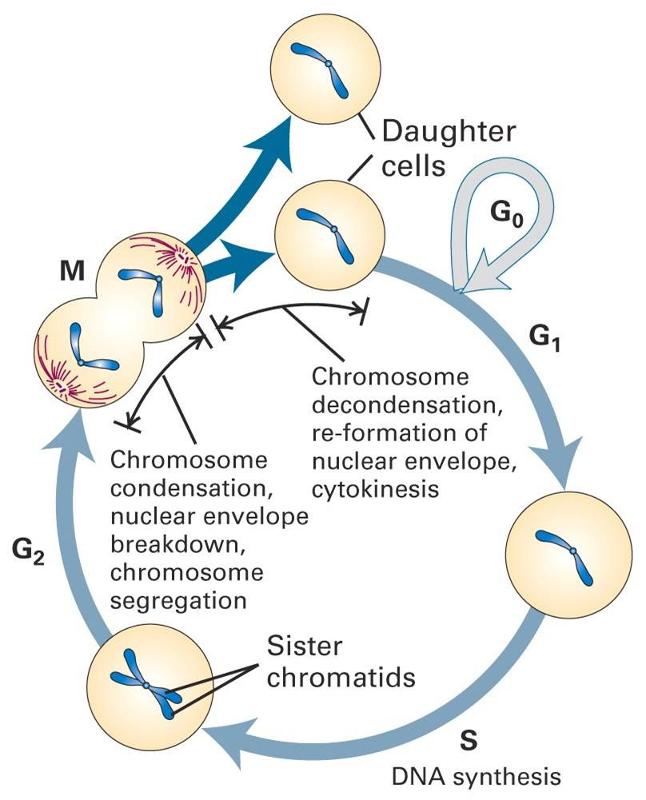
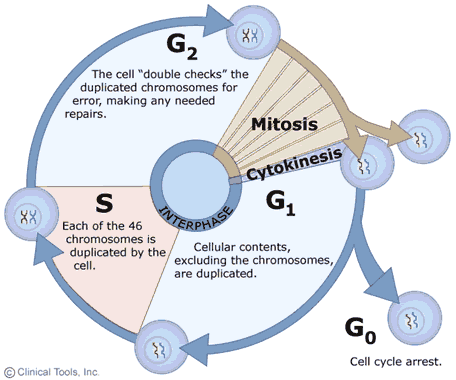
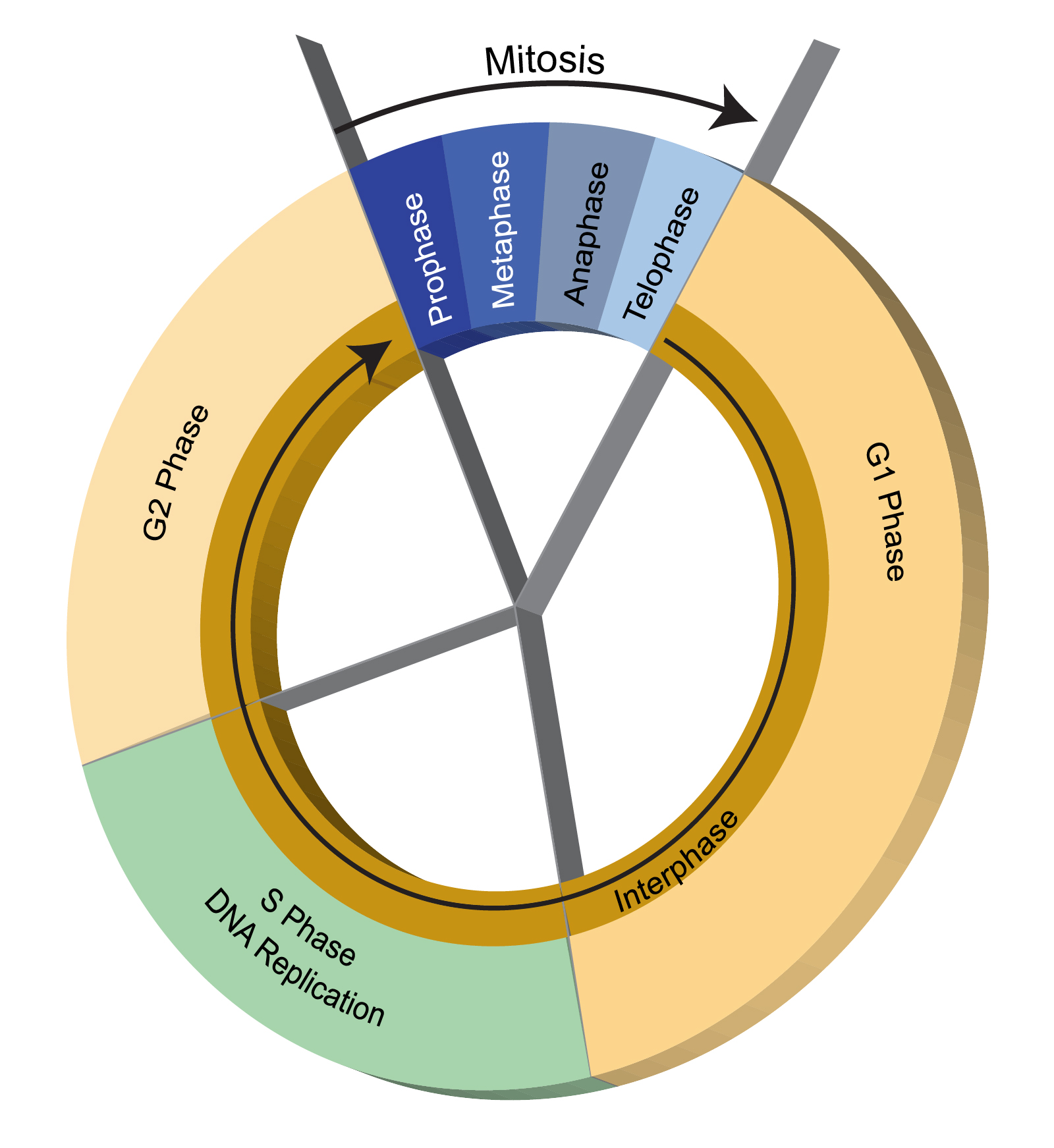
Describe The Effects Of Aging On Cell Division
The effect of hydrocortisone on DNA synthesis and cell division during aging in vitro. Gradual shortening of telomeres through cell divisions leads to aging on the cellular level and may limit lifetimes.
 Cell Cycle Arrest An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cell Cycle Arrest An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ageing or aging see spelling differences is the process of becoming olderThe term refers especially to humans many other animals and fungi whereas for example bacteria perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortalIn the broader sense ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing cellular senescence or to the.
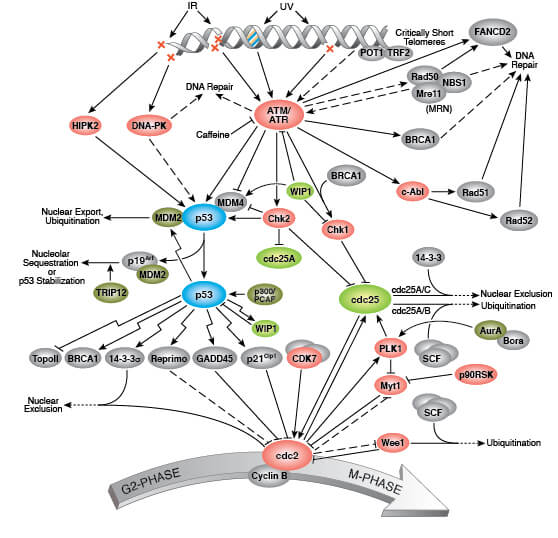
Describe the effects of aging on cell division. As aging continues waste products build up in tissue. Mice mutant for the mitotic checkpoint protein BubR1 develop age-related ailments including muscle wasting spinal curvature cataracts fat loss cardiac arrhythmia stiffening of the arterial walls and thinning of the skin. Aging is characterized by the declining ability to respond to stress increased homeostatic imbalance and increased risk of aging-associated diseases including cancer and heart disease.
More apoptosis rate occurs as the age proceeds. The hormone appears to exert its effect by increasing the fraction of cells in the proliferating pool and this increase is. Cellular aging is the result of a progressive decline in the proliferative capacity and life span of cells and the effects of continuous exposure to exogenous influences that result in the progressive accumulation of cellular and molecular damage.
To test the effect of killing off senescent cells on the aging process the investigators turned to a mouse model in which aging is dramatically accelerated. The accumulation of senescent cells contributes to aging because it leads to reduced tissue renewal and repair. The effect requires a minimum of between 12 and 18 hr exposure of the cells to hydrocortisone.
They become larger and are less able to divide and multiply. This effect is expressed during a single growth cycle by an increased rate of proliferation and a higher rate of incorporation of 3HdT into DNA. Several studies conducted in both mice and humans on mutant p53 genes have supported the notion that increased cancer protection by p53 can also lead to a shortened life life span.
This behavior can be explained by the overexpression of proteins blocking the cellular cycle or the accumulation of DNA damage on stem cells2223. Altered gene expression gradually causes the loss of tissue function which results in aging. With aging tissues dont regenerate as well due to the slowdown of cell division and the lack of stem cells replacement.
When the telomeres. Among other changes there is an increase in pigments and fatty substances inside the cell lipids. 219 Describe the effects of aging on cell division McGraw Hill Review Guide 6 from BIOL 2301 at Houston Community College.
The hormone appears to exert its effect by increasing the fraction of cells in the proliferating pool and this increase is expressed at all levels of serial subcultivation population ages. Errors in cell division lead to the altered expression of a collection of key genes in the cells. Thats what happens when free radicals which are unstable molecules that can damage DNA arent balanced by antioxidants in your body.
The mice also accumulate p16. Structural and Biochemical Changes with Cellular Aging. Studies with varying amounts of serum suggest that the hormone affects the cells by amplifying the serum signal which is the primary signal for cell division.
Many cells lose their ability to function or they begin to function abnormally. The cell division occurs more slowly with mitochondrial degeneration. As well when you grow older your cells experience more oxidative stress.
Following the arrest of cell division p53 will also induce either cell death through apoptosis or permanent loss the ability of a cell to proliferate senescence. Mitochondrial dysfunction cellular senescence stem cell exhaustion altered intercellular communication. When the telomeres become critically short the cell dies.
The elasticity in blood supplying arteries is lower and the extracellular matrix with collagen fibers and elastic connective tissue fibres will be less flexible as the aging proceeds. All cells experience changes with aging. Hydrocortisone 14 muM added to cultures of human diploid fibroblast-like cells extends the lifespan of the population.
The result is cell damage which contributes to many of the changes that accompany aging.
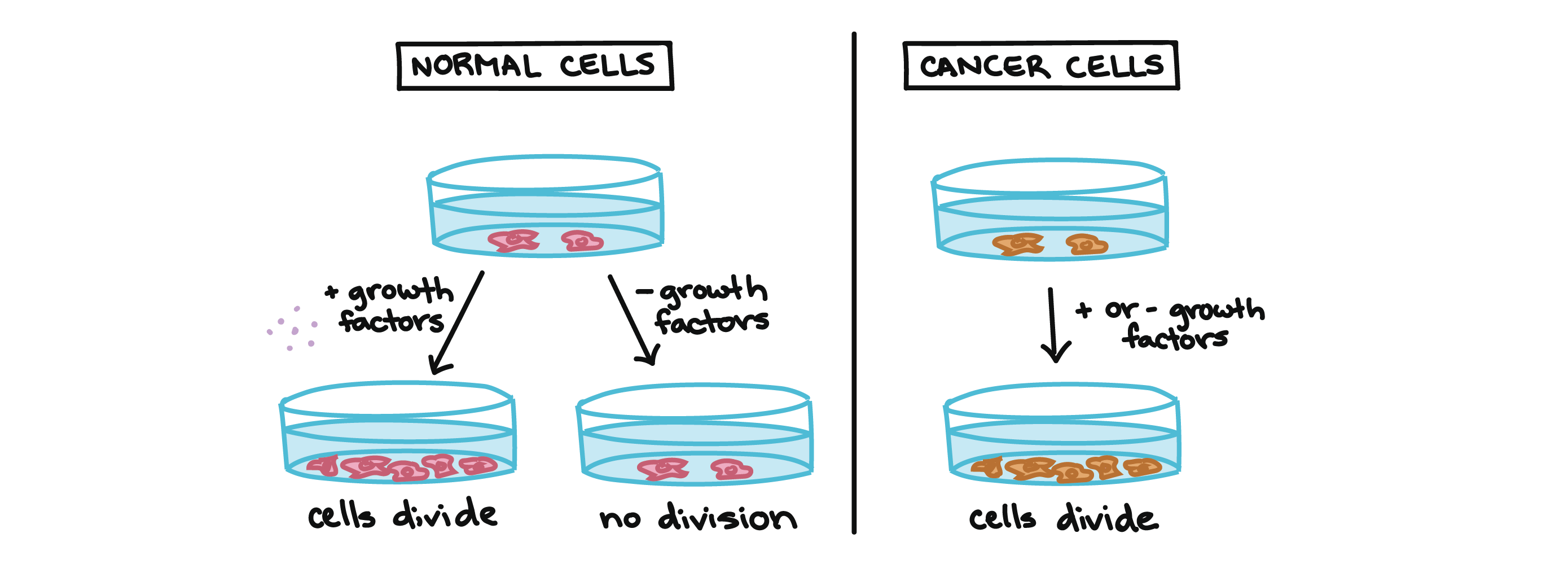 Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
 Cell Cycle Labelling Schematic Representation Of The Cell Cycle And Download Scientific Diagram
Cell Cycle Labelling Schematic Representation Of The Cell Cycle And Download Scientific Diagram
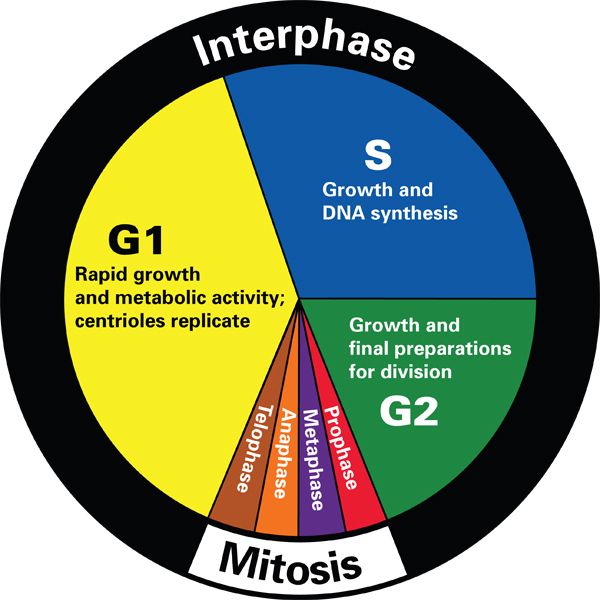 Teaching The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Carolina Com
Teaching The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Carolina Com
 Cell Division Rates Slow Down In Old Age Technology Networks
Cell Division Rates Slow Down In Old Age Technology Networks
The Cell Cycle Duration Of The Cell Cycle Sparknotes
How Long Do The Different Stages Of The Cell Cycle Take
 Overview Of Cellular Senescence And Aging Cell Signaling Technology
Overview Of Cellular Senescence And Aging Cell Signaling Technology
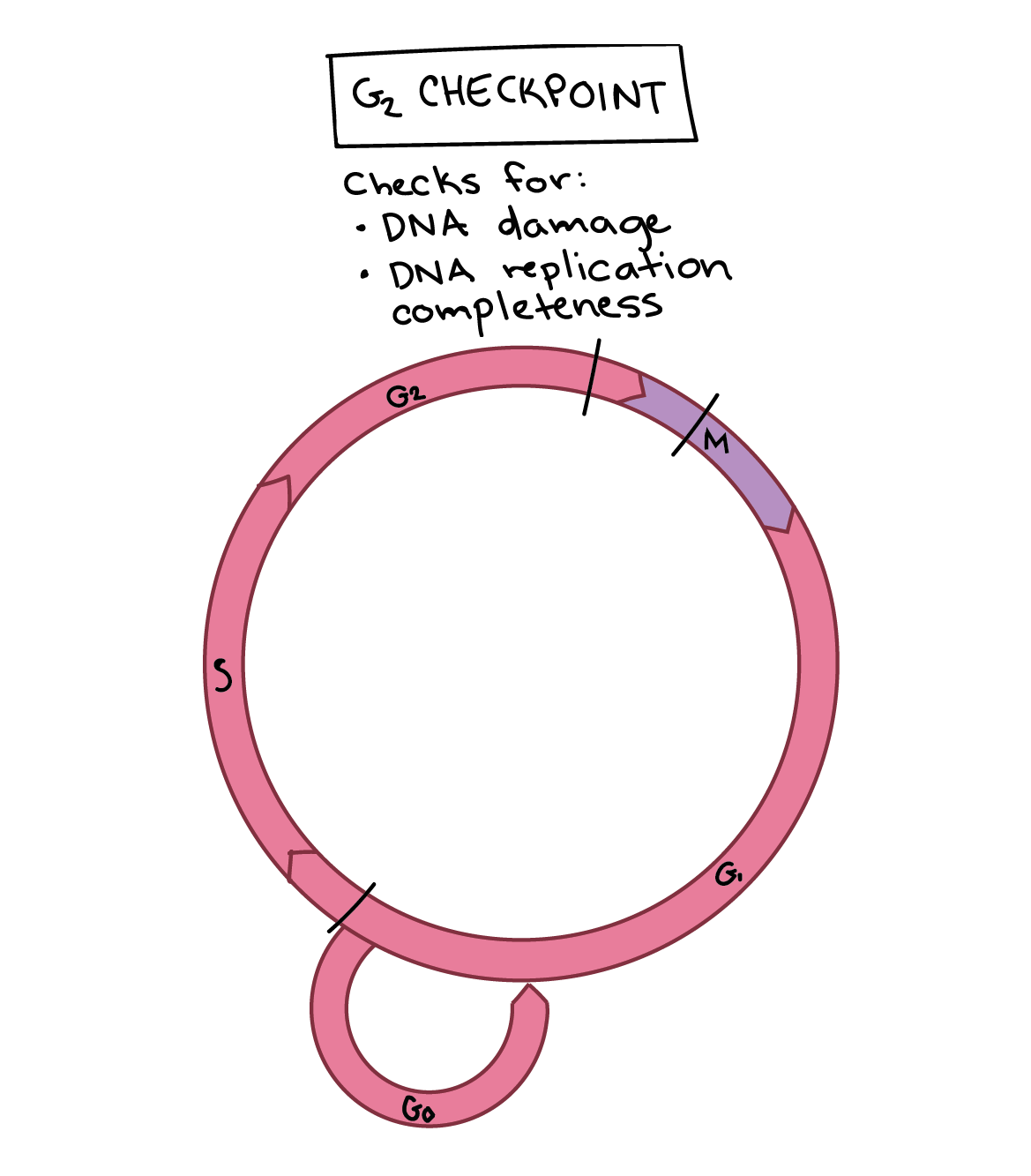 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Article Khan Academy
 Phase Separation In Cell Division Sciencedirect
Phase Separation In Cell Division Sciencedirect
Module 2 Part C Cell Division And Reproduction
 What Limits Cell Division Biology Class Study Com
What Limits Cell Division Biology Class Study Com
 Aging Cell Division Learn Science At Scitable
Aging Cell Division Learn Science At Scitable
 Are Telomeres The Key To Aging Telomeres Molecular Genetics Cell
Are Telomeres The Key To Aging Telomeres Molecular Genetics Cell
 10 2b The Mitotic Phase And The G0 Phase Biology Libretexts
10 2b The Mitotic Phase And The G0 Phase Biology Libretexts