Cell Division Growth Of An Embryo
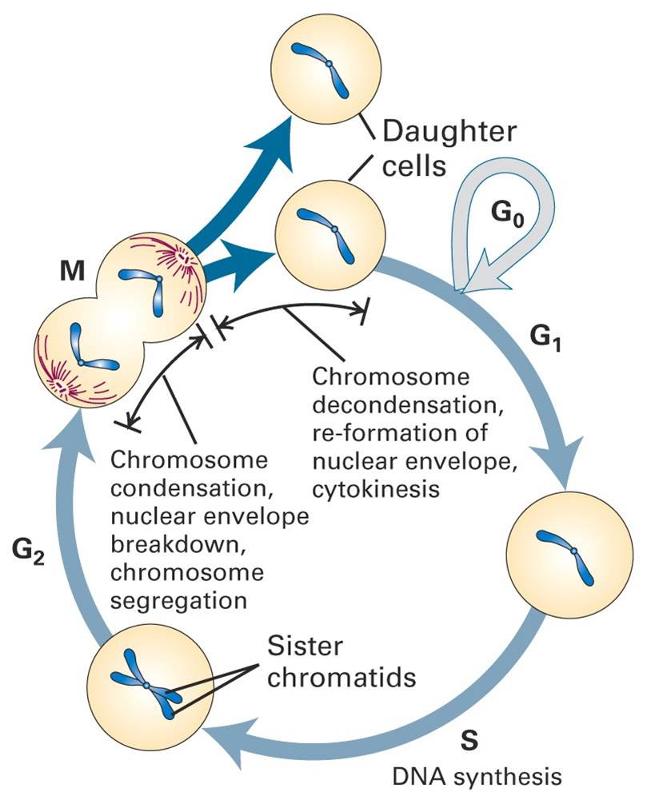
The genetic material of the. Mitosis is the form of cell division in all cells except germ cells occurs by 2 mechanical processes that initially divide the nucleus then the cell cytoplasm.
 Asynchronous Cell Cycle Phase Key To Critical Stage Of Animal Embryonic Development
Asynchronous Cell Cycle Phase Key To Critical Stage Of Animal Embryonic Development
These tissues differentiate into organs like the brain heart limbs and spinal cord.

Cell division growth of an embryo. In the C13 line seeds failed to germinate. The endoderm forms the yolk sac which will supply the growing embryo with nutrients and a source of blood supply until the formation of the placenta is complete. How quickly does a chick embryo grow.
The cells of the embryo continuously divide and re-divide to form three distinct layers called as germ layers. During this phase all embryonic cells look similar in their cytoplasmic structures and many cells also begin to make short distance migrations away from the their sister cells through a process that has been termed global cell sorting. So by continuous mitosis these cells differentiate into various tissues like the nervous tissue and muscle tissue.
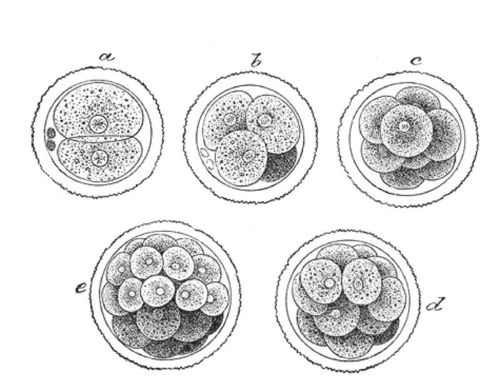
The five independent transgenic lines with the highest levels of the mutant cdc2a affected embryo formation. The morula a collection of around 30 cells blastomere is created at about 96 hours. Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis refers to the development and formation of the human embryo.
In mammal reproduction after fertilization has taken place the zygote travels down the fallopian tube while dividing to form more cells2 without the zygote actually gaining in size. Each mitosis of a diploid cell produces 2 diploid cells. Early proliferation events span from 0 to 150 min.
Remember that the way any embryo develops is by repeated cell division. It starts off as a single cell which spilts into two. Between the remaining cells the amniotic cavity is formed the bottom of which is composed of prismatic cells called the ectoderm and forms a structure called the embryonic disk.
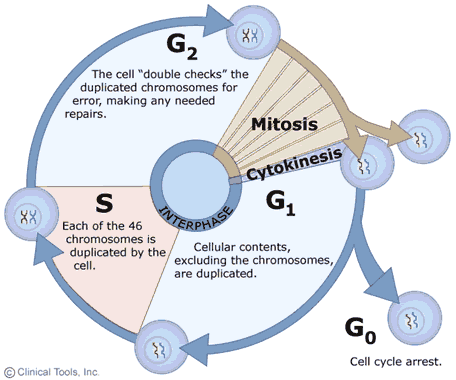
In the first stages of embryonic development a single-celled zygote undergoes many rapid cell divisions called cleavage to form a blastula which looks similar to a ball of cells. In multicellular organisms it is the means of tissue growth and maintenance. Historically the cells produced by this division are called daughter cells.
Each embryo starts development as a zygote a single cell resulting from the fusion of gametes ie. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell. Normal cell division in all cells except germ cells occurs by 2 mechanical processes that initially divide the nucleus then the cell cytoplasm.
Cell - Cell - Cell division and growth. In unicellular organisms cell division is the means of reproduction. The cells of the ectoderm gradually descend to meet.
In biological terms the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. The embryonic disk then begins to change conformation and forms a pore with the yolk sac. Each of those two cells then splits into two and so on.
Note that DNA duplication replication occurs during interphase S phase before mitosis and not. Because these cells arise only through the cleavage of the zygote and all are found inside the pellucid zone which cannot expand no growth is seen. Approximately 24 hours after fertilization the impregnated oocyte begins with the first cleavage division.
These are the ectoderm endoderm and mesoderm. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. This is achieved by the highly regulated process of cell proliferation.
These layers differentiate into various types of tissues and then organs in the later fetal development stages. The growth and division of different cell populations are regulated in different ways. The frequencies of cell division were reduced exclusively during embryo development of Arabidopsis by the expression of a dominant cdc2a mutant.
Fertilization of a female egg cell by a male sperm cell. Survival of the eukaryotes depends upon interactions between many cell types and it is essential that a balanced distribution of types be maintained. After fertilization the single cell embryo begins a series of highly stereotyped cell divisions.
This process produces two daughter cells that should be genetically identical to the parent cell. We have illustrated this schematically with a square box representing the initial egg cell.
 Cell Growth Division Mitosis Meiosis Mrs Holes Biology Class Meiosis Cell Cycle Cell Growth
Cell Growth Division Mitosis Meiosis Mrs Holes Biology Class Meiosis Cell Cycle Cell Growth
 How Cells Coordinate Growth And Division Sciencedirect
How Cells Coordinate Growth And Division Sciencedirect
 A Definition Of Cell Growth And Cell Division B Schematic Of Download Scientific Diagram
A Definition Of Cell Growth And Cell Division B Schematic Of Download Scientific Diagram
 Abscission Couples Cell Division To Embryonic Stem Cell Fate Sciencedirect
Abscission Couples Cell Division To Embryonic Stem Cell Fate Sciencedirect
 Human Fertilization And Early Development Video Khan Academy
Human Fertilization And Early Development Video Khan Academy
 From Clocks To Dominoes Lessons On Cell Cycle Remodelling From Embryonic Stem Cells Padgett 2020 Febs Letters Wiley Online Library
From Clocks To Dominoes Lessons On Cell Cycle Remodelling From Embryonic Stem Cells Padgett 2020 Febs Letters Wiley Online Library
 Asymmetric And Formative Divisions Pattern The Arabidopsis Embryo A Download Scientific Diagram
Asymmetric And Formative Divisions Pattern The Arabidopsis Embryo A Download Scientific Diagram
 Cell Division Teaching Resources The Science Teacher
Cell Division Teaching Resources The Science Teacher
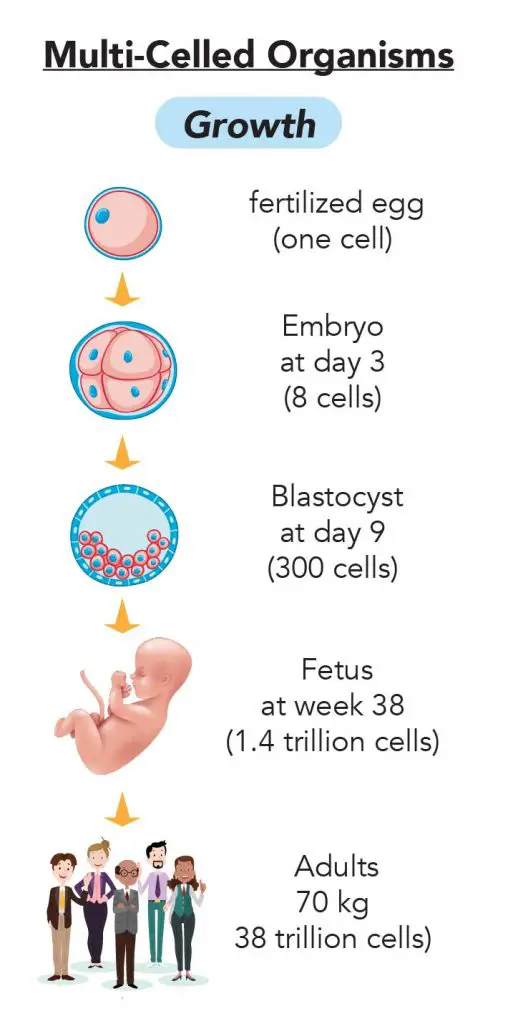 Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
 Pin By Clare Pierson On We Of The Human Species And Earth Embryonic Development Stages Of Fetal Development Fetal Development
Pin By Clare Pierson On We Of The Human Species And Earth Embryonic Development Stages Of Fetal Development Fetal Development
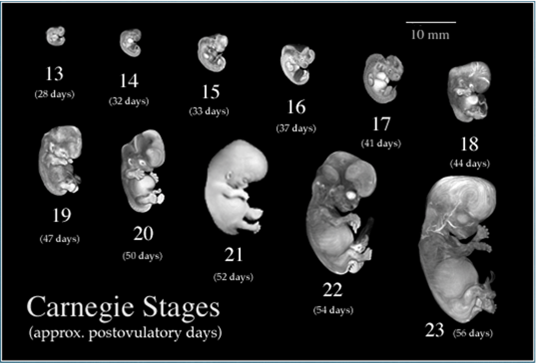 Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Biol3530 Molecular And Developmental Biology Growth And Post Embryonic Development
Plant Development Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Function Process System Different Organisms Dna Organs Cycle
 Time Lapse Images Of Embryo Cell Division Are Giving Ivf Researchers New Clues Consult Qd
Time Lapse Images Of Embryo Cell Division Are Giving Ivf Researchers New Clues Consult Qd
Biol3530 Developmental Biology Growth