Unicellular Organisms Grow By Cell Division
Growth therefore cannot be taken as a defining property of living organisms. Multicellular organism by means of tissue growth and maintainance MEIOSIS CELL DIVISION a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half creating four haploid cells each genetically distinct from the parent cell that gave rise to them.
 Pin On Science For Secondary Grades Biology Chemistry Physics And More
Pin On Science For Secondary Grades Biology Chemistry Physics And More
Cell division also plays a role in the growth and development of an organism and repairs injuries.

Unicellular organisms grow by cell division. In unicellular organisms growth is a stage in the process of their reproduction. Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation where a cell known as the mother cell grows and divides to produce two. Unicellular organisms use cell division to reproduce.
Unicellular organisms also grow by cell division. However this kind of growth exhibited by non-living objects is by accumulation of material on the surface while in living organisms growth is from inside. Multicellular organisms use cell division for growth and reproduction.
Cell division and growth. Cell division is also used to create gametes that are used in. Does a unicellular organism grow by increasing its number of cells.
It consists of a stepwise and ordered increase in the size of the cytoplasm including the increase in the number eg ribosomes mitochondria or duplication of organelles chromosomes centrosomes cell nuclei etc. For unicellular organisms cell division is important for the reproduction of the population Unicellular organism mainly use cell division also called binary fission for pollution growth. Unlike in multicellular organisms increases in cell size cell growth and reproduction by cell division are tightly linked in unicellular organisms.
This is because unicellular organisms are only composed of one cell. In multicellular organisms it is the means of tissue growth and. Jan 242021 - In 1 ncert on page 4 it is written that unicellular organisms GROW by cell division.
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell including both cytoplasmic nuclear and organelle volume. In multicellular organisms cell division assists in the formation of gametes which combine to produce organisms. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation.
Cell division serves as a means of cell reproduction in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms use cell division for growth and repair of damage such as wounds. A unicellular organism is an organism that consists of a single cellThis means all life processes such as reproduction feeding digestion and excretion occur in one cellAmoebas bacteria and plankton are just some types of unicellular organismsThey are typically microscopic and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
This is achieved by the highly regulated process of cell proliferation. In unicellular organisms reproduction takes place through binary fission which is a type of mitotic division. The growth and division of different cell populations are regulated in different ways.
Survival of the eukaryotes depends upon interactions between many cell types and it is essential that a balanced distribution of types be maintained. In unicellular organisms cell division is the means of reproduction. Cell division results in reproductiongrowth replacement and recycling of the organism.
The first microscope was made in the late 1800s. EduRev NEET Question is disucussed on EduRev Study Group by 160 NEET Students. Shouldnt it be MULTIPLY instead if grow.
Cell - Cell - Cell division and growth. In multicellular organisms as the founders of the cell theory determined almost two centuries ago growth consists of the growth of the number of cells in the process of development. Cell division causes increase in the number of cells composing the organism hence its growth in size.
An organism only grows by increasing its number of cells. In unicellular organisms cell division is the means of reproduction. Unicellular organisms do respond to their environment.
Bacteria grow to a fixed size and then reproduce through binary fission a form of asexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms it is the means of tissue growth and maintenance. Non-living objects also grow if we take increase in body mass as a criterion for growth.
The new cells produced by cell division are.
 Intro To Cells Reading Covering Division Of Labor Stem Cell Develop And Differentiation Your Body I Learning Science History Articles Teacher Lesson Plans
Intro To Cells Reading Covering Division Of Labor Stem Cell Develop And Differentiation Your Body I Learning Science History Articles Teacher Lesson Plans
 Dinoflagellates Have A Haplontic Life Cycles Life Cycles Cycle Life
Dinoflagellates Have A Haplontic Life Cycles Life Cycles Cycle Life
 Purpose Of Cell Division Biology Dictionary
Purpose Of Cell Division Biology Dictionary
Protista Basic Unicellular Organisms
2 Growth And Division In Multicellular Vs Unicellular Organisms How Download Scientific Diagram
 Cell Cell Division And Growth Biology Britannica Com Human Digestive System Human Body Bones Human Body
Cell Cell Division And Growth Biology Britannica Com Human Digestive System Human Body Bones Human Body
 For Simple Unicellular Organisms Such As The Amoeba One Cell Division Is Equivalent To Reproduction An Entire New Orga Cell Division Cell Cycle Cell Biology
For Simple Unicellular Organisms Such As The Amoeba One Cell Division Is Equivalent To Reproduction An Entire New Orga Cell Division Cell Cycle Cell Biology
 Unicellular Multicellular Science Cells 5th Grade Science Science Education
Unicellular Multicellular Science Cells 5th Grade Science Science Education
 Intro To Cells Reading Covering Unicellular Multicellular Composed Microscopic Living Things Come In Ma Learning Science Time Lessons Teacher Lesson Plans
Intro To Cells Reading Covering Unicellular Multicellular Composed Microscopic Living Things Come In Ma Learning Science Time Lessons Teacher Lesson Plans
 How Can Unicellular Organism Grow By Cell Division Because Cell Division Is Their Mode Of Reproduction So If They Grow That Should Be In Means Of Size Or Mass But In Ncert
How Can Unicellular Organism Grow By Cell Division Because Cell Division Is Their Mode Of Reproduction So If They Grow That Should Be In Means Of Size Or Mass But In Ncert
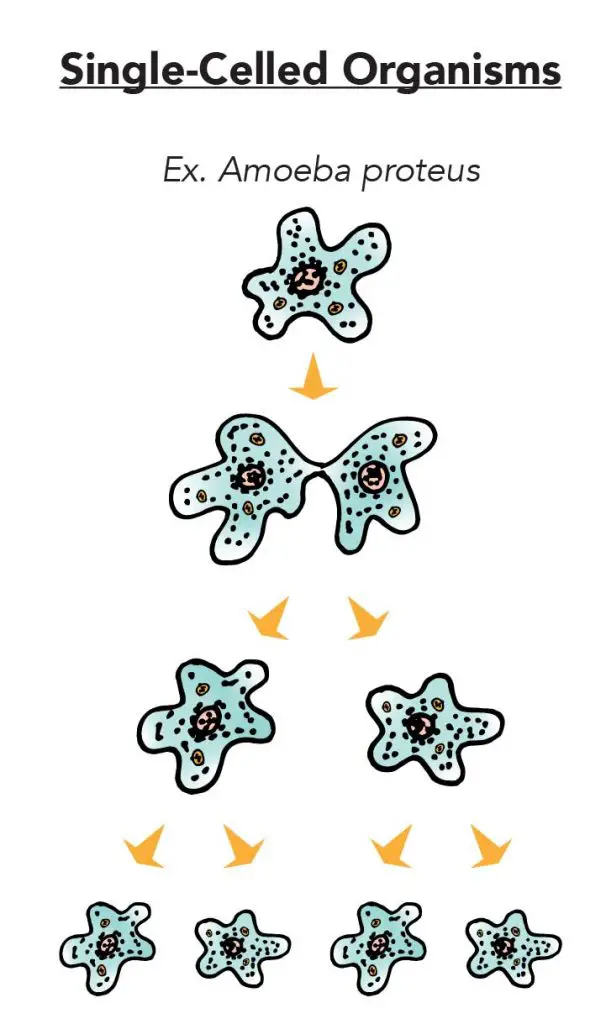 Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
Why Cell Division Is Important Rs Science
 Characteristics Of Living Organisms Biology Notes For Igcse 2014 Biology Notes Cell Respiration Body Systems
Characteristics Of Living Organisms Biology Notes For Igcse 2014 Biology Notes Cell Respiration Body Systems
 What Is An Amoeba What Is All Biology Diagrams Cells Project Classical Conversations Homeschool
What Is An Amoeba What Is All Biology Diagrams Cells Project Classical Conversations Homeschool
 Ap Biology 2007 2008 Biology Is The Only Subject In Which Multiplication Is The Same Thing As Division Ap Biology Cell Cycle Cell Division
Ap Biology 2007 2008 Biology Is The Only Subject In Which Multiplication Is The Same Thing As Division Ap Biology Cell Cycle Cell Division
 Cell Division Boundless Biology
Cell Division Boundless Biology
 Life Cycles A Unicellular Life Cycle As Seen In Species Like Download Scientific Diagram
Life Cycles A Unicellular Life Cycle As Seen In Species Like Download Scientific Diagram
 Unicellular Organism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Unicellular Organism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle And Mitosis The Key Roles Of Cell Division Cell Division Functions In Reproduction Growth And Rep Cell Cycle Mitosis Cell Division
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle And Mitosis The Key Roles Of Cell Division Cell Division Functions In Reproduction Growth And Rep Cell Cycle Mitosis Cell Division
 Cell Reproduction Worksheet Answers With The Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet Answers Fresh Cell Division And Cell Cycle Cell Division Color Worksheets
Cell Reproduction Worksheet Answers With The Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet Answers Fresh Cell Division And Cell Cycle Cell Division Color Worksheets