Asymmetric Cell Division Review
Generally one cell is a stem cell while the other cell is a differentiated cell. This review examines divergent mechanisms of ACD across different kingdoms.
 Lessons From Development A Role For Asymmetric Stem Cell Division In Cancer Sciencedirect
Lessons From Development A Role For Asymmetric Stem Cell Division In Cancer Sciencedirect
These are called asymmetric cell divisions whether or not asymmetry is morphologically evident at the time of division.

Asymmetric cell division review. A detailed mechanistic understanding of ACD is therefore necessary to understand cell fate decisions in health and disease. Provides a review of the recent evidence of symmetric divisions in mammalian intestinal stem cells spermatogenesis and epithelial tissues such as hair follicles. Elaborate cellular mechanisms that orchestrate the processes required for asymmetric cell divisions are often shared between stem cells and other asymmetrically dividing cells.
During the development of an organism asymmetric stem cell division predominates. ACD can be manifested in the biased segregation of macromolecules the differential partitioning of cell organelles or differences in sibling cell size or shape. These new findings reveal that contrary to the previous thinking adult tissue stem cells are often lost eg.
Asymmetric cell division ACD is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism used by prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike to control cell fate and generate cell diversity. These two cells have different sizes different morphology and different gene expression. Disruption of the machinery that regulates asymmetric division may be a reason for the generation of cancer.
In contrast an ACD is defined as cell division creating two qualitatively distinct daughter cells Figure 1b. Asymmetric cell division ACD a mechanism for cell-type diversification in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes is accomplished through highly coordinated cell-fate segregation genome partitioning and cell division. In interphase Par proteins set up a polarity axis 18.
The guard cells are generated in specific cell files. During asymmetric cell division cells must establish asymmetrypolarity which is guided by varying degrees of intrinsic versus. Asymmetric cell divisions are traditionally divided into two flavors.
Alternatively they can orient their division plane so that only one of the two daughter cells maintains contact with the niche and stem cell identity. The Process of Asymmetric Cell Division Stem cells can either divide symmetrically or asymmetrically. This exchange results in movement of the SMC nucleus toward the site of GMC contact followed by asymmetric division of the SMC with an unusual curved cell wall.
Asymmetric cell divisions in these files produce guard mother cells GMCs which then divide symmetrically to form the two guard cells. Alternatively the division. Symmetric cell division is defined as the generation of daughter cells that are destined to acquire the same fate.
In mitosis this axis is used for spindle orientation. To generate the multitude of different cell types requires cell divisions in which daughter cells have different fates. When a mother stem cell divides asymmetrically it produces two qualitatively distinct daughter cells with different fates.
The asymmetric cell division of stem cells which produces one stem cell and one differentiating cell has emerged as a mechanism to balance stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. The difference in daughter cells may be due to unequal partitioning of factors in the mother cell such that all or most are inherited by only one daughter. These distinct pathways have been elucidated mostly in Drosophila.
What is Asymmetric Stem Cell Division. Although the molecules involved are highly conserved in vertebrates the way they act is tissue. A simple model of asymmetric cell division postulates that it is a three-step process.
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs articles conference papers preprints and more on ASYMMETRIC CELL DIVISION. The asymmetric mechanism is maintained by cell polarity factors cell fate determinants and the spindle apparatus. By differentiation and replaced in a stochastic manner.
The mutation or dysregulation of these. To achieve this remarkable task they can undergo an intrinsically asymmetric cell division whereby they segregate cell fate determinants into only one of the two daughter cells. In a symmetric cell division SCD the mother cell creates two daughter cells with equal cel l fates Figure 1a.
These events are usually preceded by and. Before the GMC divides however it sends a polarizing signal to the subsidiary mother cells SMCs in the neighboring files. Asymmetric stem cell division is a central characteristic of stem cells.
This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise to daughter cells of equivalent fates. Notably stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells. In principle there are two mechanisms by which distinct properties may be conferred on.
Differences can be mediated. Find methods information sources references or conduct a literature. An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates.
One copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate. The process of asymmetric cell division was originally described almost 100 1years ago by Conklin who found that during division of early ascidian embryos an area of yellow cytoplasm always. Whereas important paradigms have arisen from the study of animal embryonic divisions the strategies for choreographing the dynamic subprocesses are in fact highly varied.
Stem cells divide asymmetrically to generate one daughter with a stem-cell fate and one daughter with different fate.
 The Scarecrow Gene Regulates An Asymmetric Cell Division That Is Essential For Generating The Radial Organization Of The Arabidopsis Root Cell
The Scarecrow Gene Regulates An Asymmetric Cell Division That Is Essential For Generating The Radial Organization Of The Arabidopsis Root Cell
 Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Divisions In The Asymmetric Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Divisions In The Asymmetric Download Scientific Diagram
 A New Role For Notch In Control Of Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Of Developing T Cells Biorxiv
A New Role For Notch In Control Of Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Of Developing T Cells Biorxiv
 Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Cell Division In Epithelial Cells Schematic Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Cell Division In Epithelial Cells Schematic Download Scientific Diagram
 Obligatory Asymmetric Replication Asymmetric Cell Division
Obligatory Asymmetric Replication Asymmetric Cell Division
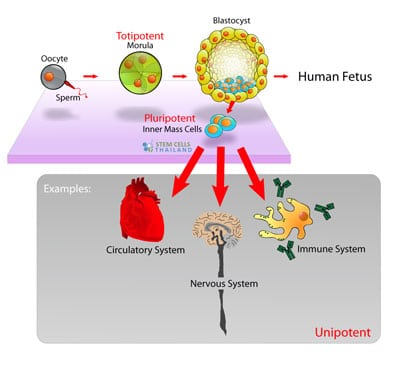
 Fig 2 1 Schematic Presentation Of Stem Cell Function A The Differentiation Potential Of A Stem Cell Determines Its Potency B The Balance Between Symmetric And Asymmetric Cell Divisions Regulates Stem Cell Self Renewal
Fig 2 1 Schematic Presentation Of Stem Cell Function A The Differentiation Potential Of A Stem Cell Determines Its Potency B The Balance Between Symmetric And Asymmetric Cell Divisions Regulates Stem Cell Self Renewal
 Egfr Aurka Signaling Rescues Polarity And Regeneration Defects In Dystrophin Deficient Muscle Stem Cells By Increasing Asymmetric Divisions Sciencedirect
Egfr Aurka Signaling Rescues Polarity And Regeneration Defects In Dystrophin Deficient Muscle Stem Cells By Increasing Asymmetric Divisions Sciencedirect
 Protein Complex Assemblies In Epithelial Cell Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Sciencedirect
Protein Complex Assemblies In Epithelial Cell Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Sciencedirect
 Basl Controls Asymmetric Cell Division In Arabidopsis Cell
Basl Controls Asymmetric Cell Division In Arabidopsis Cell
 Dynamics Of Asymmetric And Symmetric Divisions Of Muscle Stem Cells In Vivo And On Artificial Niches Sciencedirect
Dynamics Of Asymmetric And Symmetric Divisions Of Muscle Stem Cells In Vivo And On Artificial Niches Sciencedirect
 Evidence Of Asymmetric Cell Division And Centrosome Inheritance In Human Neuroblastoma Cells Pnas
Evidence Of Asymmetric Cell Division And Centrosome Inheritance In Human Neuroblastoma Cells Pnas
 Francois Schweisguth Cell Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Research Institut Pasteur
Francois Schweisguth Cell Polarity And Asymmetric Cell Division Research Institut Pasteur
 Roles And Regulations Of Hippo Signaling During Preimplantation Mouse Development Sasaki 2017 Development Growth Amp Differentiation Wiley Online Library
Roles And Regulations Of Hippo Signaling During Preimplantation Mouse Development Sasaki 2017 Development Growth Amp Differentiation Wiley Online Library
 Asymmetric Cell Division An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Asymmetric Cell Division An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Download Scientific Diagram
Symmetric And Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Download Scientific Diagram
 Membrane And Organelle Dynamics During Cell Division Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
Membrane And Organelle Dynamics During Cell Division Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
 Regulators Of Asymmetric Cell Division In Breast Cancer Trends In Cancer
Regulators Of Asymmetric Cell Division In Breast Cancer Trends In Cancer
 Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
Mechanisms Of Asymmetric Stem Cell Division Cell
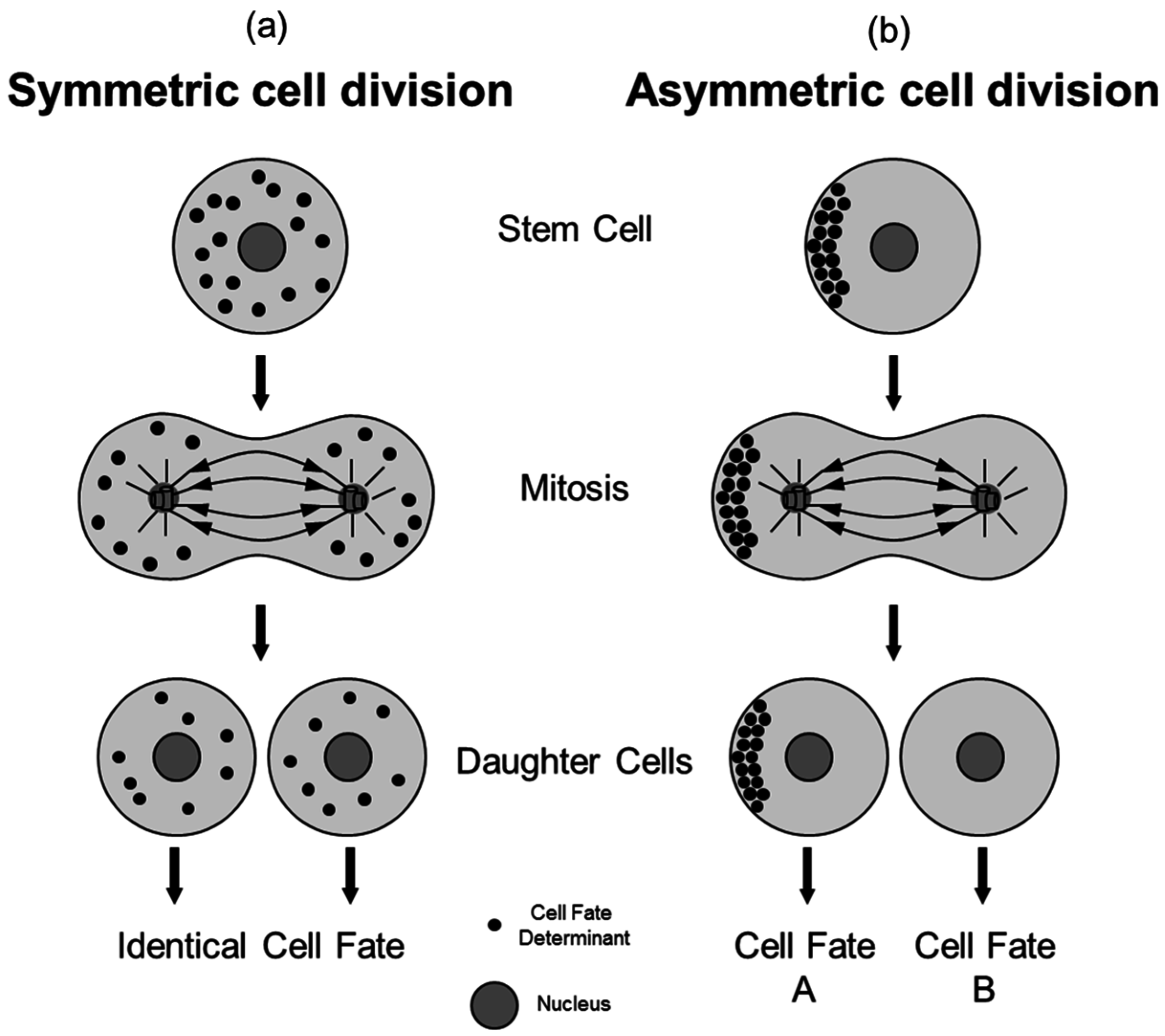 Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html
Symmetry Free Full Text Concise Review Asymmetric Cell Divisions In Stem Cell Biology Html