Dynein In Cell Division
Our results show that posterior epidermal cells are polarized with dynein protein anteriorly localized undergo dynein-dependent spindle rotation and divide along the anteroposterior axis. Genetic studies in Drosophilaand mouse have demonstrated that dynein function is essential in metazoan organisms.
 Cytoplasmic Dynein During Mitosis Sciencedirect
Cytoplasmic Dynein During Mitosis Sciencedirect
OConnell and Wang 2000.

Dynein in cell division. In yeast it was proposed that dynein offloads directly from the MT plus ends to the cell cortex by an active MT-mediated delivery Markus and Lee 2011 a process which requires the neck region of dynein. A recent study of cytoplasmic dynein gene knockout mice demonstrated that in CyDn cells the Golgi complex is fragmented and widely distributed in the cytoplasm and late endosomes are. Recent genetic and biochemical findings have illuminated the cellular roles of dynein and dynactin and.
A central challenge in the field is to understand how a single motor can transport such a diverse array of cargoes and how this process is regulated. Dynein has critical roles both in interphase and during cell division. Once the spindle is aligned by dynein DNA is distributed equally.
Cytoplasmic dynein-1 hereafter referred to as dynein is a major microtubule-based motor critical for cell division. Since the initial discovery of cytoplasmic dynein it has become apparent that this microtubule-based motor is involved in several cellular functions including cell division and intracellular transport. In humans males produce 500000000 day.
Intestinal cells divide every 3 days are broken down by digestion blood cells last 3 months are replaced by new cell division nerve cells usually dont divide last for life Embryo. Dynein is involved in the movement of chromosomes and positioning the mitotic spindles for cell division. Here we focus on interphase cargoes of dynein which include membrane-bound organelles RNAs protein complexes and viruses.
Our results show that posterior epidermal cells are polarized with dynein protein anteriorly localized undergo dynein-dependent spindle rotation and divide along the anteroposterior axis. Longer neck regions allow enhanced off-loading without affecting motor activity while shorter necks block delivery to the cortex. A striking feature of dynein is that despite having a wide variety of functions the catalytic subunit is coded in a single gene.
Cytoplasmic dynein is a multisubunit minus-enddirected microtubule motor that serves multiple cellular functions. Dynein carries organelles vesicles and possibly microtubule fragments along the axons of neurons toward the cell body in a process called retrograde axoplasmic transport. More recently evidence has accumulated that LC8 also interacts with proteins that are not clearly connected with dynein or microtubule-based transport including some with roles in apoptosis viral pathogenesis enzyme regulation and kidney development.
The molecular basis by which each cargo is linked to dynein and its cofactor dynactin has started to emerge. Dynein is essential for the formation and positioning of the mitotic spindle as well as the transport of various cargos in the cell. Our findings therefore provide an important insight into the role of oriented cell division in tissue morphogenesis.
Another multisubunit complex dynactin may be required for most if not all cytoplasmic dynein-driven activities and may provide clues to dyneins functional diversity. This led to the proposal that a conformational. Almost constant cell division.
Dynein motors move the mitotic spindle to the cell division plane in many cell types including in budding yeast in which dynein is assisted by numerous factors including the microtubule-associated protein MAP She1. LC8 was first discovered as an essential component of the microtubule-based molecular motor dynein and as such is involved in fundamental processes including retrograde vesicular trafficking ciliaryflagellar motility and cell division. This cell division facilitates constriction around the embryos circumference only in the posterior region and epithelial bending formation.
During mitosis dynein localizes at the cell cortex Kiyomitsu and Cheeseman 2012. Sex cells are unique. To perform various cellular activities there seem to be different types of dynein that share a common catalytic.
Our findings therefore provide an important insight into the role of oriented cell division in tissue morphogenesis. Of particular importance for this. During cell division dynein positions the mitotic spindle a complex apparatus that allows cells to segregate genetic material.
This cell division facilitates constriction around the embryos circumference only in the posterior region and epithelial bending formation.
 Figure 19 28 Structure Of Ciliary And Flagellar Axonemes Cell Biology Biology Biology Notes
Figure 19 28 Structure Of Ciliary And Flagellar Axonemes Cell Biology Biology Biology Notes
 Kinetochore Microtubule Attachment Educacion
Kinetochore Microtubule Attachment Educacion
 Dynein Dynamics At The Microtubule Plus Ends And Cortex During Division In The C Elegans Zygote Biorxiv
Dynein Dynamics At The Microtubule Plus Ends And Cortex During Division In The C Elegans Zygote Biorxiv
 Schematic Diagram Of Cytosolic Dynein And The Dynactin Heterocomplex Cell Biology Student Living Organelles
Schematic Diagram Of Cytosolic Dynein And The Dynactin Heterocomplex Cell Biology Student Living Organelles
 Mechanisms Of Spindle Positioning Cell Biology How To Memorize Things Rockefeller University
Mechanisms Of Spindle Positioning Cell Biology How To Memorize Things Rockefeller University
 Functions And Mechanics Of Dynein Motor Proteins Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
Functions And Mechanics Of Dynein Motor Proteins Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
 Structure Of Ciliary And Flagellar Axoneme T S Axoneme Cilia Flagella In 2020 Cell Biology Prokaryotic Cell Biology
Structure Of Ciliary And Flagellar Axoneme T S Axoneme Cilia Flagella In 2020 Cell Biology Prokaryotic Cell Biology
 Two Models For The Formation Of Aggresomes Cell Journal Cell Biology Rockefeller University
Two Models For The Formation Of Aggresomes Cell Journal Cell Biology Rockefeller University
 Cilia Flagella Structure Motile Organelles Of Eukaryotic Cells Common Structure Regardless Of Beating Mechanica Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell Cell Parts
Cilia Flagella Structure Motile Organelles Of Eukaryotic Cells Common Structure Regardless Of Beating Mechanica Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell Cell Parts
 Roles Of Cytoplasmic Dynein During Mitosis Sciencedirect
Roles Of Cytoplasmic Dynein During Mitosis Sciencedirect
 Cilia Flagella Structure A Tubule B Tubule Each Of The Paired Outer Microtubules Has An A And A B Tubule Axonemal Dynei Biologia Biologia Celular Celulas
Cilia Flagella Structure A Tubule B Tubule Each Of The Paired Outer Microtubules Has An A And A B Tubule Axonemal Dynei Biologia Biologia Celular Celulas
Schematic Drawing Of Cell Cycle Dependent Dynamic Behavior Of Download Scientific Diagram
 Basal Body Google Search Fun Science Organelles Cell Division
Basal Body Google Search Fun Science Organelles Cell Division
 Neural Crest Delamination In The Context Of The Cell Cycle In The Neuroepithelium Cell Cycle Cycle The Cell
Neural Crest Delamination In The Context Of The Cell Cycle In The Neuroepithelium Cell Cycle Cycle The Cell
 Structure And Functions Of Cilia And Flagella Cell Theory Plant And Animal Cells Plasma Membrane
Structure And Functions Of Cilia And Flagella Cell Theory Plant And Animal Cells Plasma Membrane
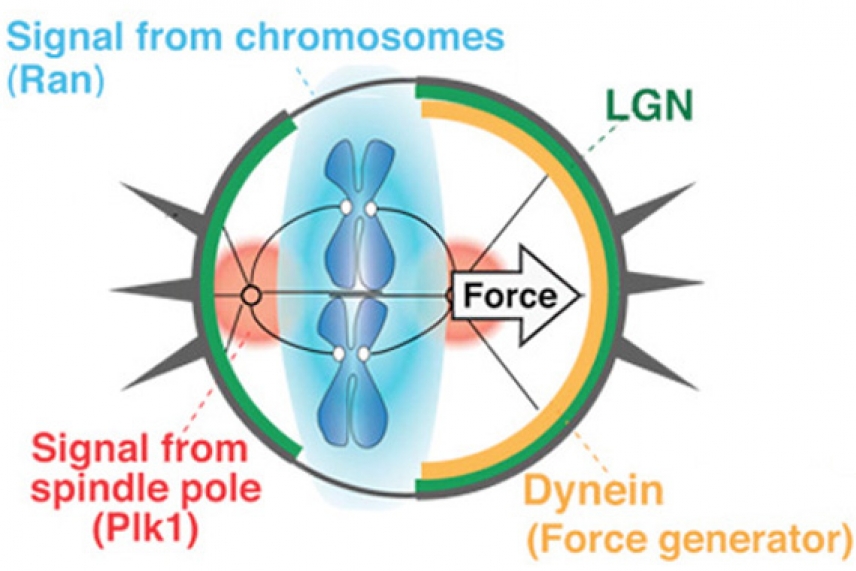 A Mitosis Mystery Solved How Chromosomes Align Perfectly In A Dividing Cell Whitehead Institute
A Mitosis Mystery Solved How Chromosomes Align Perfectly In A Dividing Cell Whitehead Institute
 Model Numa Spatially Targets Dynein Activity To Minus Ends At Mitosis Download Scientific Diagram
Model Numa Spatially Targets Dynein Activity To Minus Ends At Mitosis Download Scientific Diagram

